Figure 2.
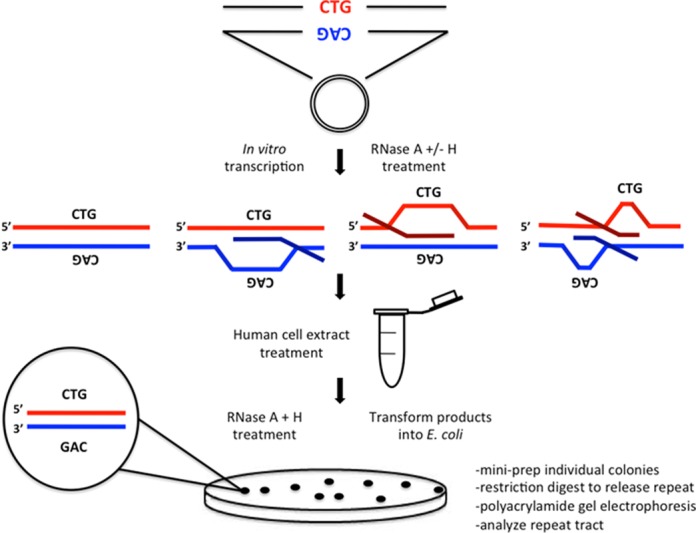
R-loop instability assay. Plasmids bearing an expanded (CAG)79·(CTG)79 repeat tract were in vitro transcribed and treated with the appropriate RNase to produce R-loop templates of each configuration as schematically depicted. R-loop templates were subsequently treated with human (HeLa) cell extract to allow processing to occur. Nucleic acid products were extracted and subjected to a final RNase A+H treatment to remove any residual R-loop products and transformed into E. coli bacteria and plated overnight. Individual colonies were picked (representing individual products of R-loop processing) and minimally cultured (see Materials and Methods). DNA was then extracted and restriction digested to release the repeat tract. Products were electrophoresed alongside known size markers to determine repeat length.
