Figure 8.
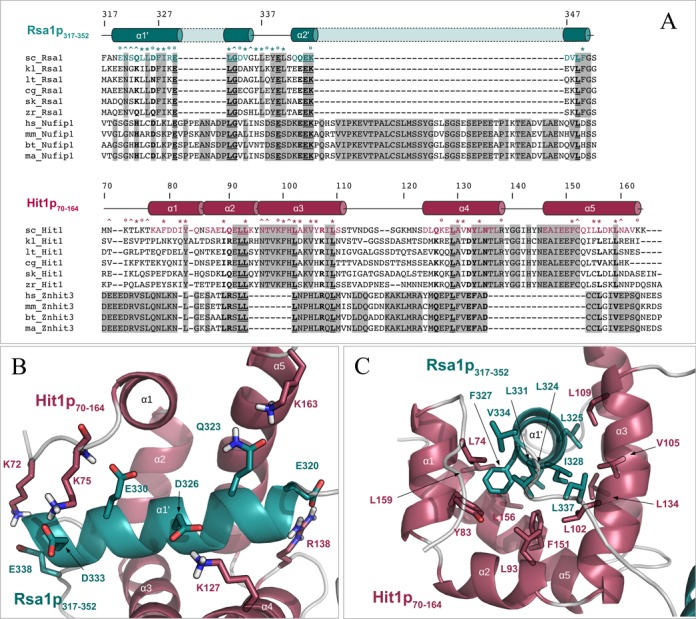
The protein–protein interface between Rsa1p317−352 and Hit1p70−164 is maintained by hydrophobic and polar contacts involving conserved residues. (A) Multiple amino acid sequence alignments of proteins Rsa1/NUFIP1 and Hit1/ZNHIT3 present in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (sc_), Kluyveromyces lactis (kl_), Lachancea thermotolerans (lt_), Candida glabrata (cg_), Saccharomyces (Lachancea) kluyveri (sk_), Zygosaccharomyces rouxii (zr_), Homo sapiens (hs_), Mus musculus (mm_), Bos taurus (bt_) and Macaca mulatta (ma_), and constructed using CLUSTALW. Strictly matching residues in yeast or in mammals are highlighted using gray squares. Strictly conserved inter-species positions are underlined and highlighted in bold. Inter-species residues with groups of strongly similar properties are indicated in bold. Secondary structures extracted from the Rsa1p317−352−Hit1p70−164 3D structure are represented above the protein sequences, using cylinders for α-helices and lines for loops. Residues located at the interface between the two proteins (according to an intermolecular distance cut-off of 3.5 Å) are highlighted using circles, stars and carets for charged, mainly hydrophobic and neutral to polar amino acids respectively. (B) and (C) Representation of some hydrophobic (B) and polar (C) contacts located at the protein–protein interface of the Rsa1p317−352−Hit1p70−164 complex. Non-polar hydrogens are not represented.
