Figure 1.
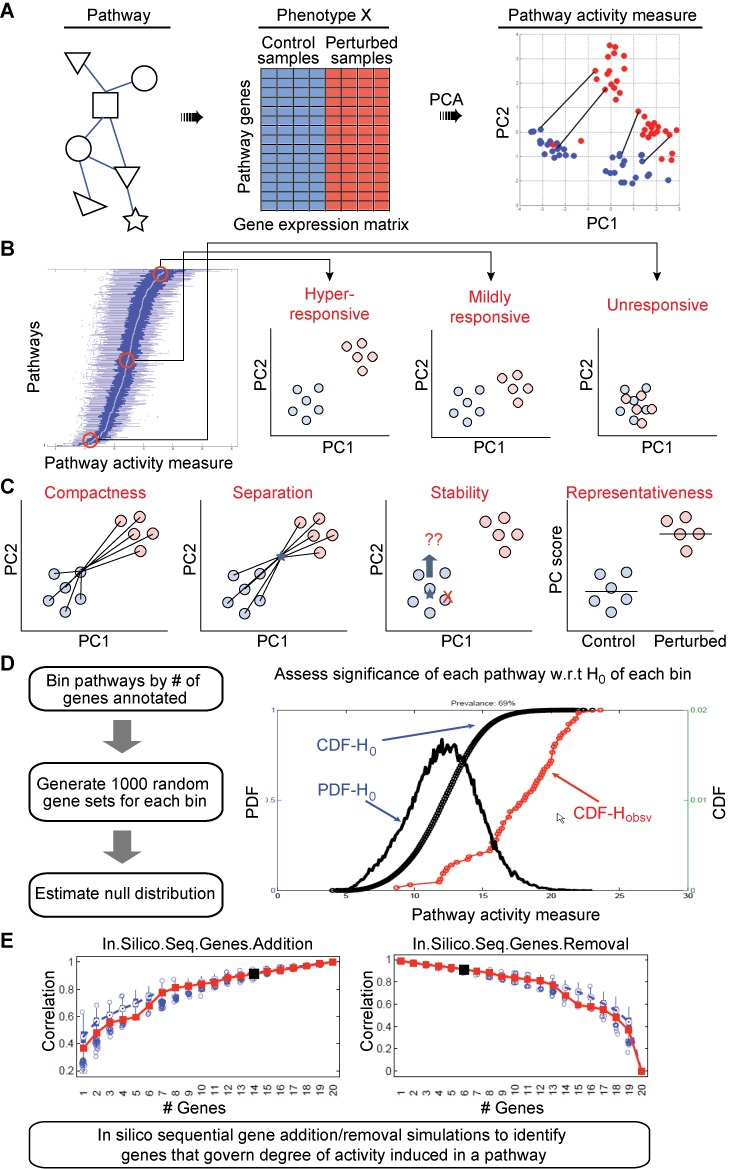
A framework for pathway activity inference. (A) A PCA-based clustering framework is used to assess the phenotypic separation between the basal and perturbed states. The degree of activity induced is quantified by computing the Euclidean distance between paired samples. (B) Based on the distribution of activity induced in samples from the perturbed group, the pathways are ranked as hyper-responsive, mildly responsive and unresponsive. (C) Four clustering-based summary statistics are computed to assess the magnitude and significance of induced activity. (D) Significance of observed activity is compared with that estimated for a random gene set with comparable number of genes. (E) Up to 1000 in silico simulations are executed in which genes are sequentially added or removed to identify the minimum set of genes that would recover 90% or more of the pathway activity level observed with the full set.
