Figure 4.
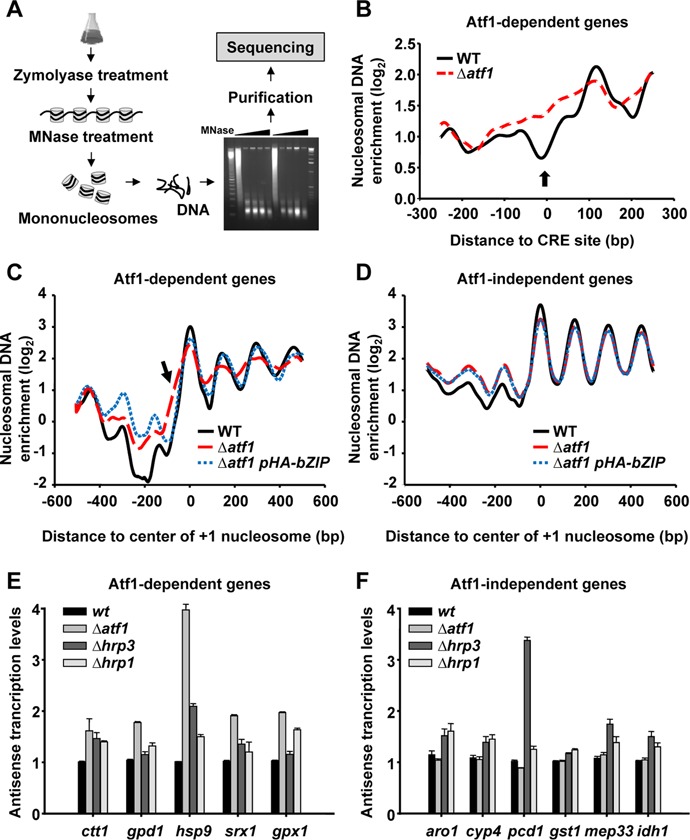
The regularly organized nucleosome arrays in stress coding regions are disrupted in the Δatf1 strain causing enhanced antisense transcription. (A) Scheme depicting the MNase-seq assay. (B) Composite plots of relative nucleosome occupancy for strains 972 (WT) and MS98 (Δatf1). Thirty five stress genes were aligned at their CRE sites and the average of their log2 nucleosome occupancy was plotted. (C) Composite plots of relative nucleosome occupancy for strains 972 (WT), MS98 (Δatf1) and EP203.bZIP (Δatf1 pHA-bZIP). The genes represented in (B) were aligned at their +1 nucleosome and the average of their log2 nucleosome occupancy data was plotted. (D) Fifty Atf1-independent genes were aligned as in (C). (E and F) The expression levels of antisense transcripts in strains 972 (WT), MS98 (Δatf1), EP110 (Δhrp3) and IV69 (Δhrp1) for Atf1-dependent (ctt1, gpd1, hsp9, srx1 and gpx1; E) and -independent (aro1, cyp4, pcd1, gst1, mep33 and idh1; F) genes were analysed by reverse transcription-qPCR. The graphs show the amount of transcripts of each gene relative to that in the wild-type strain. Error bars (SEM) were calculated from biological triplicates.
