Figure 1.
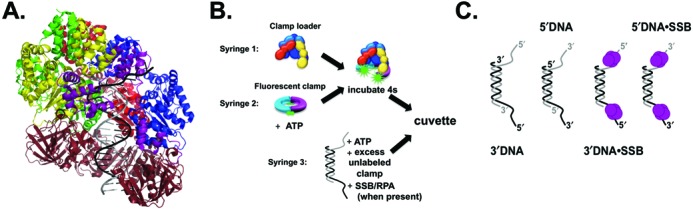
(A) DNA binding by clamp loaders. Duplex DNA spirals inside the cap of the clamp loader, with the single-stranded portion exiting between a gap in the clamp loader subunits (bacteriophage T4 clamp loader, PDB ID: 3U60 (15)). (B) A diagram showing the sequential mixing scheme in the stopped-flow. A solution of clamp loader in syringe 1, is mixed with fluorescent clamp and ATP from syringe 2 for 4 s to form an ATP·clamp loader·clamp complex. This complex is mixed with DNA, excess unlabeled clamp, and ATP. When SSB or RPA are present in reactions, they are included in syringe 3 with DNA to form SSB·DNA complexes. (C) Diagrams of the DNA structures used in these studies. All DNA structures are composed of two 60-mer oligonucleotides, annealed to produce a 30-nt duplex region, with two symmetrical 30-nt overhangs on either end of the duplex region. RPA was substituted for SSB in experiments with RFC and PCNA.
