Figure 3.
Fine-Mapping of eQTL-Mu1 Identifies a Novel Insertion of AtMu1c Underlying the eQTL.
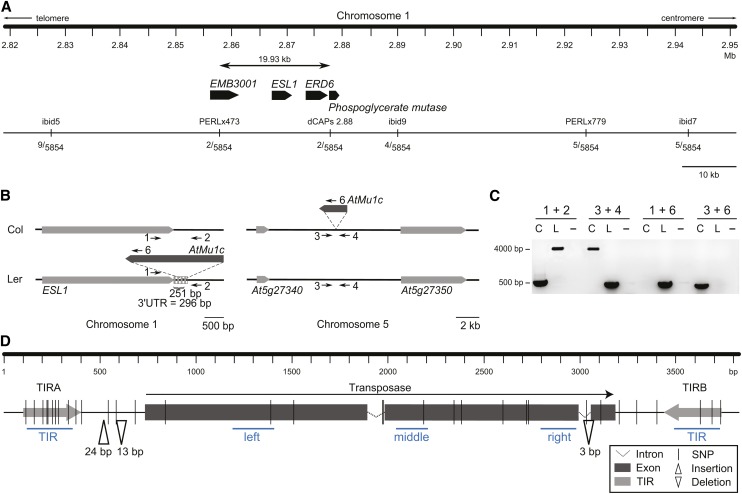
(A) Fine-mapping of eQTL-Mu1. The number of recombinants for each marker from 5854 chromosomes is shown. The mapping interval contained four protein-coding genes (At1g08910 [EMB3001], At1g08920 [ESL1], At1g08930 [ERD6], and At1g08940). None of them had a nonsynonymous SNP between Col and Ler.
(B) Schematic representation of AtMu1c insertion positions in Col and Ler. Neighboring genes, light gray; 3′ UTR, dashed box; numbered arrows indicate the primers used in (C).
(C) Products of AtMu1c amplification with flanking primers (empty site, ∼450 bp; with AtMu1c insertion, ∼4000 bp). Primer positions are indicated in (B). C, Col; L, Ler.
(D) Schematic representation of genomic sequence differences between AtMu1c(Col) and AtMu1c(Ler). Sequences were determined by sequencing multiple independent PCR products. Blue lines represent amplicons assayed in Figure 4. Primer sequences can be found in Supplemental Table 3.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]