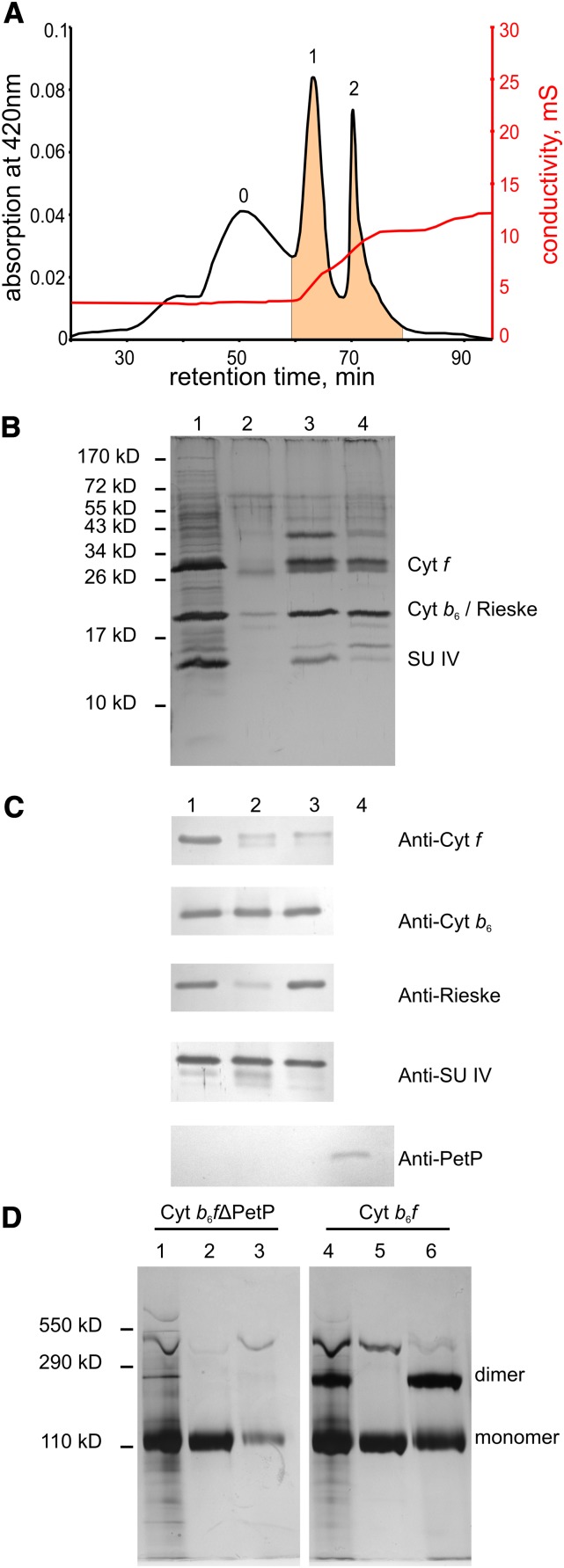
Figure 3.
Purification of the b6f Complex from the b6f-ΔpetP Mutant.
(A) Elution profile from a preparative IEC column (second purification step): peak 0, with b6f degradation forms; peak 1, b6f-monomer; peak 2, b6f-dimer. UnoQ1 (Bio-Rad), 0.5 mL/min, 4°C; gradient 1: 0 to 4.2 mM NaCl, gradient 2: 4.2 to 8.2 mM NaCl, gradient 3: 8 0.2 to 20 mM NaCl.
(B) SDS-PAGE (silver-stained) of fractions from chromatography: (1) IMAC of b6f-ΔPetP, (2) peak 0 of IEC, (3) peak 1 of IEC, and (4) peak 2 of IEC.
(C) Immunoblot analysis of Cyt b6f-ΔPetP: (1) Cyt b6f-ΔPetP-peak of IMAC, (2) IEC fraction 1 (b6f monomer), (3) IEC fraction 2 (b6f dimer), and (4) PetP heterologously expressed in E. coli as reference (synthetic peptide-antibody; Davids Biotechologie).
(D) BN-PAGE (silver-stained) of isolated b6f-ΔPetP- and WT b6f-complex: (1) b6f-ΔPetP after IMAC, (2) IEC fraction 1 (b6f-ΔPetP monomer), (3) IEC fraction 2 (b6f-ΔPetP dimer), (4) b6f after IMAC, (5) IEC fraction 1 (b6f monomer), and (6) IEC fraction 2 (b6f dimer); for details, see text.