Figure 3.
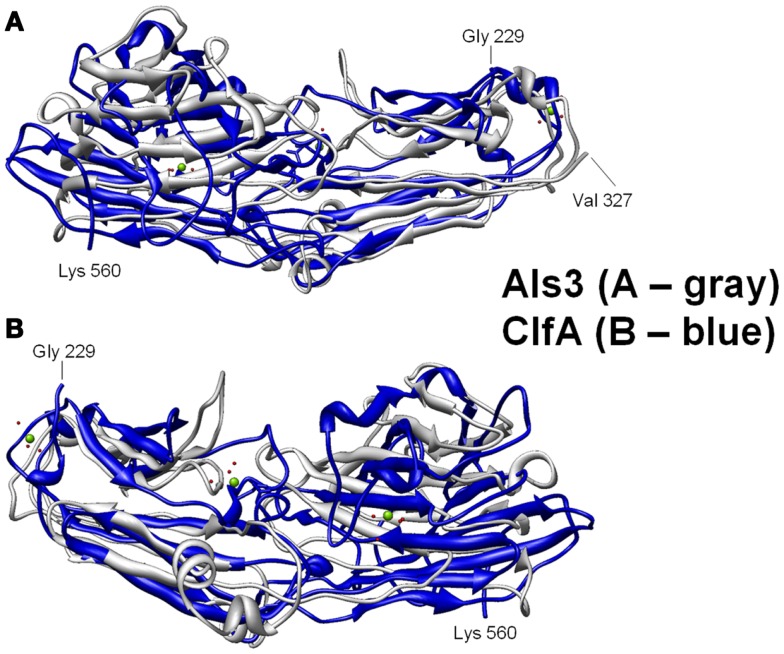
Structural basis for B-cell epitopes shared in Als3 and ClfA is shown. Combinatorial extension analysis was used to compare the model of Als3 with that of the known structure of ClfA. (A) Front view of the 3-D structural superimposition of homologous structural domains of Als3 (Candida albicans; gray) and ClfA (Staphylococcus aureus; blue); (B) rear view of the same region in protein homologs. The discovery, prediction, and validation of T-cell epitopes in such homologs offers further promise in design of innovative convergent vaccine antigens that induce efficacious cell-mediated immunity. Such striking convergence of linear (T cell) and 3-D (B-cell) epitopes in proteins with analogous functional and immunoprotective properties is consistent with the observation that C. albicans and S. aureus occupy very similar anatomic niches. It follows that humans have likely evolved common pathways of host defense against both pathogens, which may be targeted in novel vaccines that leverage convergent immunity.