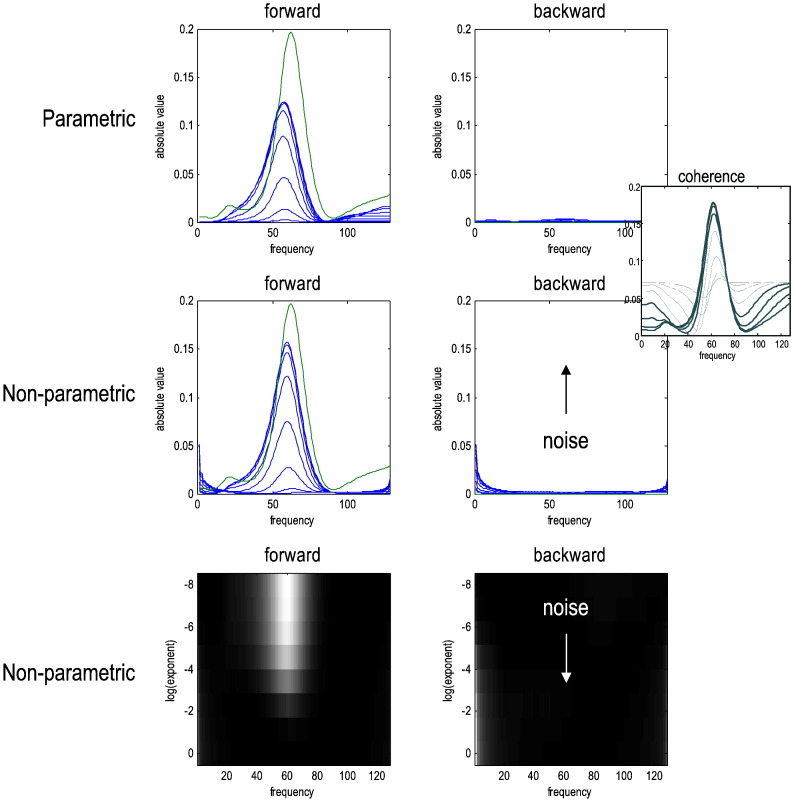
Fig. 8.
This figure uses the same format as in the previous figure; however here, we have increased the amplitude of measurement noise (from a log amplitude − 8 to − 2). This measurement noise had channel-specific and shared components at a log ratio of one (i.e., a ratio of about 2.72). At nontrivial levels of noise (with a log-amplitude of about − 4) the expected Granger causality fails for both parametric and nonparametric measures. The predominant failure is a spurious reduction in the forward spectral causality and the emergence of low-frequency backward spectral causality with nonparametric measures. The inset on the upper right shows the impact of noise on the coherence between the two channels at low (solid) and high (dotted) levels of noise.