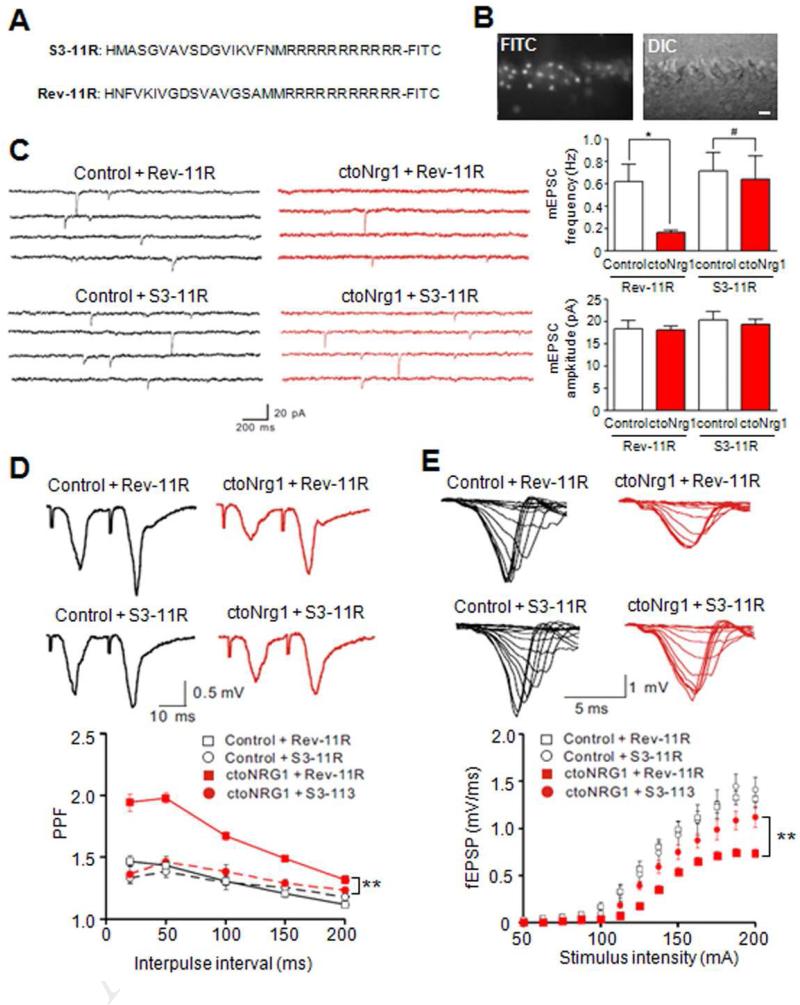
Figure 6. Inhibition of LIMK1 ameliorated glutamatergic impairment in ctoNrg1 slices.
(A) Amino acid sequences of LIMK1 control (Rev-11R) and inhibitory peptide (S3-11R).
(B) Penetration of FITC-labeled S3-11R into neurons of hippocampal slices. Bar, 20 μm.
(C) Treatment with S3-11R, but not Rev-11R, attenuated mEPSC frequency reduction in ctoNrg1 CA1 pyramidal neurons. Hippocampal slices were treated with 1 μM S3-11R and Rev-11R, respectively. Left, representative traces; right, quantitative data. Rev-11R: n = 8 cells from 3 mice per genotype, S3-11R: n = 8 cells from 3 control mice, n = 9 cells from 3 ctoNrg1 mice; * p < 0.05, # p > 0.05, one-way ANOVA.
(D) S3-11R, but not Rev-11R, reduced PPF at SC-CA1 synapses in ctoNrg1 mice. Slices were treated as in C. Top, representative traces; bottom, quantitative data. Rev-11R: n = 9 slices from 3 control mice, n = 10 slices from 3 ctoNrg1 mice, S3-11R: n = 8 slices from 3 mice per genotype; ** Genotype F (3, 155) = 88.07, p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA.
(E) Partial recovery of I/O curves at ctoNrg1 SC-CA1 synapses by S3-11R. Top, representative traces; bottom, quantitative data. Rev-11R: n = 9 slices from 3 control mice, n = 10 slices from 3 ctoNrg1 mice, S3-11R: n = 8 slices from 3 control mice, n = 9 slices from 3 ctoNrg1 mice; ** Genotype F (3, 416) = 31.32, p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA.