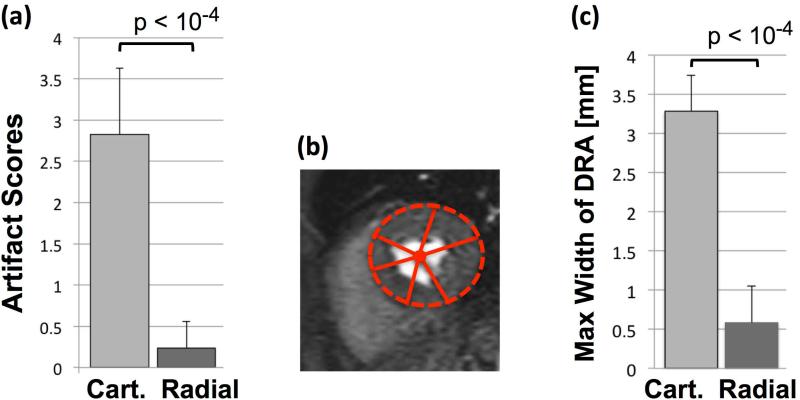
Figure 7.
(a): Summary of artifact scores for the representative first-pass perfusion images (Fig. 6) assigned by two expert readers (consensus 0-4 scale scoring; 0: no artifact, 1: negligible, 2: mild, 3: moderate, 4: severe artifact); the results clearly show the superiority of optimized radial imaging in reducing the DRA (Cartesian: 2.83±0.8 vs. optimized radial: 0.24±0.32, P<0.0001). (b): Quantification scheme for measuring the maximum width (largest transmural extent) of the dark-rim artifact along angular directions (as explained in Methods). (c) Summary of the DRA width measurements as shown in (b), indicating that the maximal width of DRA is significantly reduced with optimized radial imaging (Cartesian: 3.28±0.46 vs. optimized radial: 0.58±0.47, P<0.0001). Note that quantitative DRA measurements become less accurate for sub-pixel widths.