Figure 5.
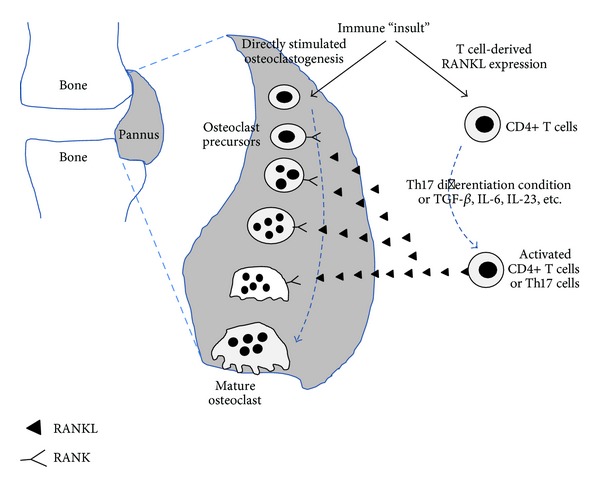
T cells are activated to produce RANKL or osteoclastogenic cytokines by various stimuli. RANKL and activated T cell-cytokines have the potential to induce osteoclastogenesis. With T cells, the outnumbered osteoclasts destroy the bone in RA.
