Fig. 3.
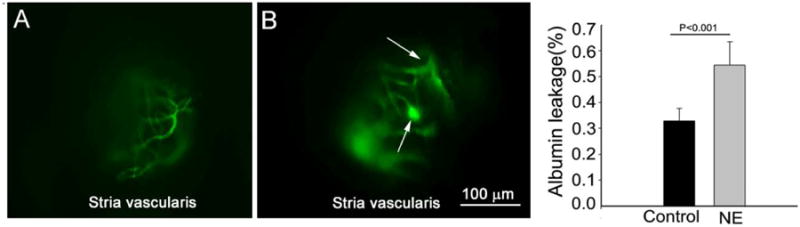
An open vessel-window preparation was used to study vascular permeability in control and noise-exposed mice. (A) shows FITC-albumin labeled blood vessel from the stria vascularis in a control animal. (B) shows FITC-albumin extravasation from leaked capillaries in a noise-exposed animal. The arrows point out the leakage sites. (C) The difference in albumin leakage in control and noise-exposed animals, seen as a general increase in the background signal, was statistically significant (n = 5, *P < 0.001).
