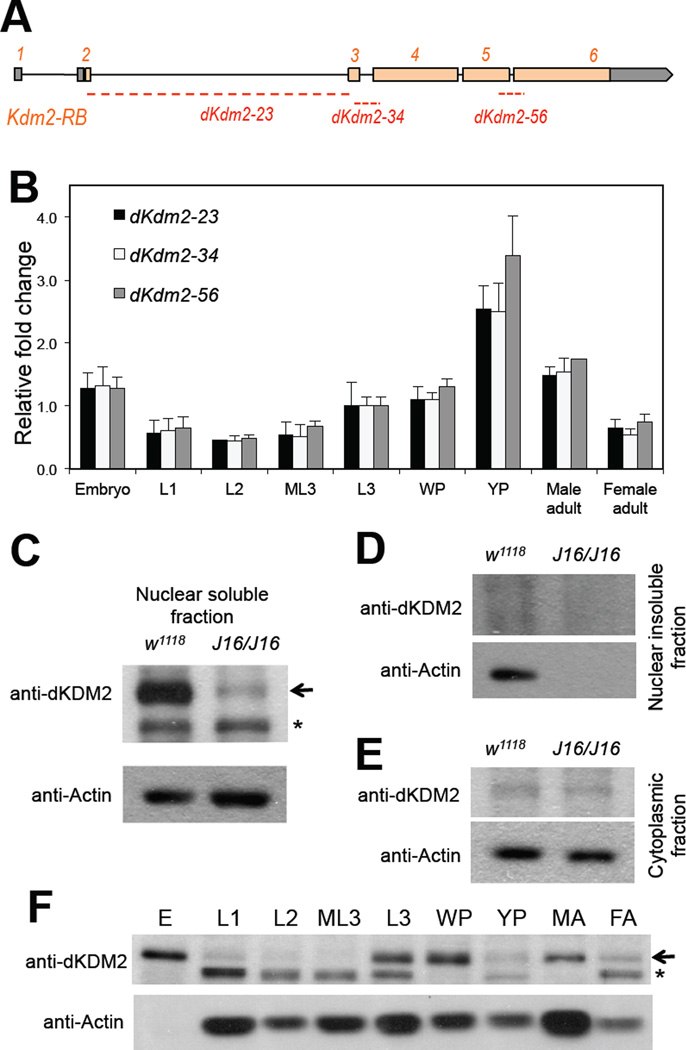
Figure 2. Expression of dKDM2 during noraml Drosophila development.
(A) Schematic view of the dKdm2 locus, showing the 6 exons with the coding exons in orange and UTR regions in grey. The three pairs of the primers used in qRT-PCR assay are shown below, and they all span the neighboring exons. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of relative expression of dKdm2 mRNA during development. L1, first instar larvae; L2, second instar larvae; ML3, mid-third instar larvae; L3, third instar larvae; WP, white pupae; YP, yellow pupae. (C ~ E) Sub-cellular localization of the dKDM2 protein assayed with immunoblotting using a polyclonal antibody. dKDM2 protein is present in the nuclear soluble fraction (C), and the dKdm2 deletion line Df(3R)J16 (see below) homozygous larvae was used as a negative control. dKDM2 protein is not present in the nuclear insoluble fraction (D) and the cytoplasmic fraction (E). (F) Levels of the dKDM2 protein in the nuclear soluble fraction of extract from different developmental stages. E, embryos; MA, male adults; FA, female adults. Equal total amount of proteins were loaded in each lane. The non-specific bands are marked with ‘*’, and anti-Actin was used as a control.