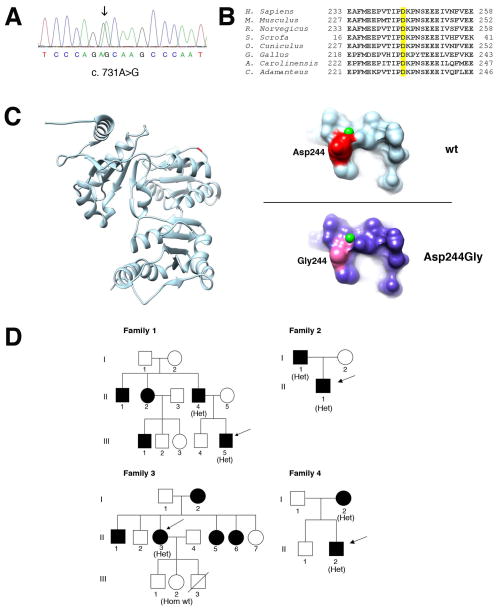
Figure 2. Genetic and molecular analysis of the p.Asp244Gly mutation.
A. Electropherogram of the CASQ1 gene sequence of one patient. The patient is heterozygous for the c.731A>G variant (arrow).
B. Phylogenetic alignment of the CASQ1 orthologs. The aspartic acid in position 244 in the human CASQ1 is highlighted yellow and is conserved in species ranging from snakes (C. Adamanteus) to humans.
C. 3D structure of human CASQ1 protein. Ribbon representation of the model of chain A of the human CASQ1 3D structure (PDB:3UOM) with the Asp244 shown in red/dark (left). On the right, detailed views of predicted surface structure of the local molecular environments surrounding the Asp244 (upper panel) or the Gly244 residues (lower panel). The small (green) spheres represent Ca2+ ions. D. Pedigrees of families. Black filled symbols represent affected family members. The genotype of individuals is shown in parenthesis as follows: Het, heterozygous for the c.731A>G variant; Hom wt, homozygous for the wild-type allele. Arrows indicate probands.