Fig. 3.
In vitro ligation assays.
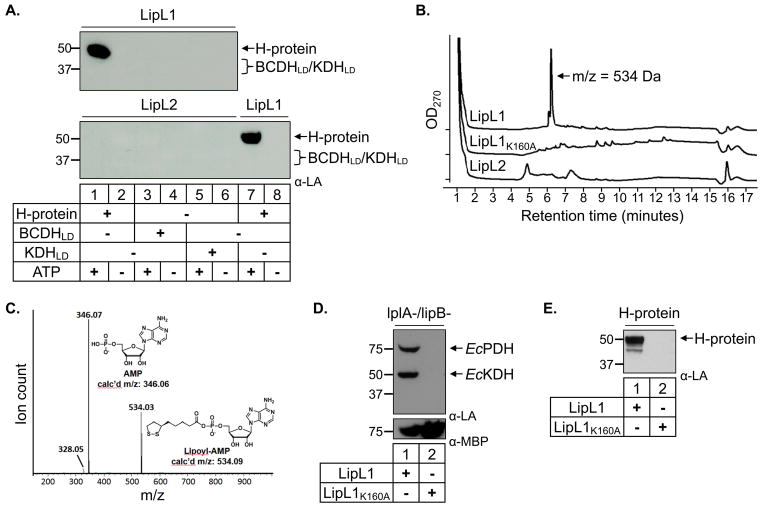
(A) Lipoate ligase activity. Western blot analysis shows that LipL1 is an ATP-dependent lipoate ligase only when H-protein is used as substrate, while LipL2 does not display lipoate ligase activity with any substrate.
(B) HPLC traces for LipL1, LipL1K160A and LipL2 adenylation reactions. Each enzyme was reacted with lipoate and ATP for 10 minutes prior to HPLC analysis with absorbance monitored at 270 nm. The LipL1 reaction produced a major product eluting at 6.2 minutes with a mass of 534 Da as determined by ESI-MS.
(C) Identification of Lipoyl-AMP produced by LipL1. The major product generated by LipL1 was subjected to collision induced dissociation MS/MS, demonstrating that this product contains AMP.
(D) JEG3 complementation by LipL1 and LipL1K160A. LipL1 is able to lipoylate endogenous E. coli substrates in lipoylation deficient strain JEG3, whereas LipL1K160A is unable to catalyze this activity. Expression of both proteins was confirmed by stripping and re-probing the blot with α-MBP (lower panel).
(E) Recombinant LipL1K160A cannot lipoylate the H-protein in an in vitro lipoylation assay.