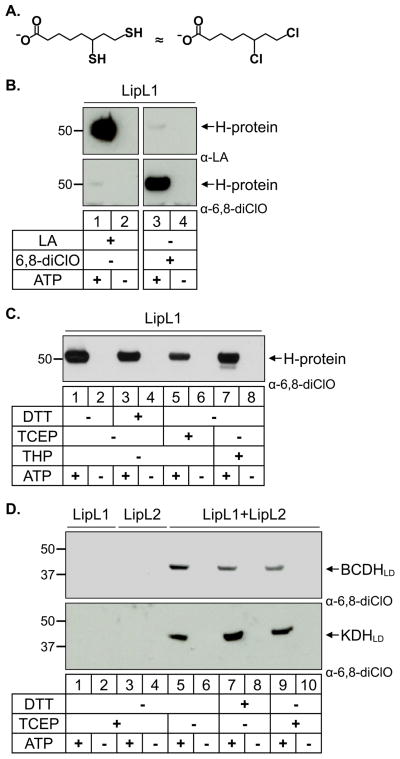
Fig. 6.
6,8-dichlorooctanoate is attached to all substrates independent of redox environment.
(A) 6,8-Dichlorooctanoate (6,8-diClO) is a structural analog of reduced lipoate (dihydrolipoate).
(B) Modification of the H-protein by lipoate and 6,8-diClO. LipL1 catalyzes the attachment of lipoate as shown in the α-LA western blot (top panels) and 6,8-diClO as shown in the α-6,8-diClO western blot (bottom panels). The α-LA antibodies and the α-6,8-diClO antiserum show very little cross-reactivity.
(C) Effect of reducing conditions on the enzymatic activity of LipL1 against the H-protein. The H-protein is modified by 6,8-diClO independent of the redox environment.
(D) Effect of reducing conditions on the enzymatic activity of LipL1 + LipL2. BCDHLD and KDHLD are modified by 6,8-diClO independent of the redox environment.