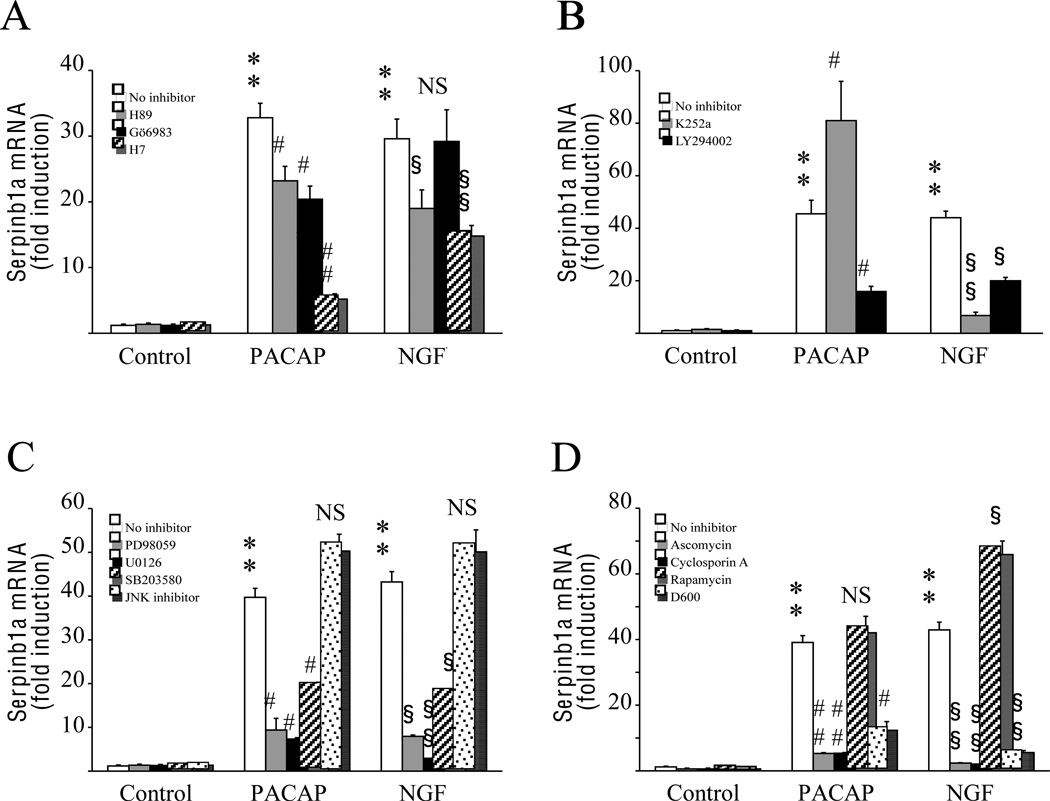
Fig. 3.
Investigation of the transduction pathways involved in the regulation of serpinb1a expression by PACAP and NGF in PC12 cells. Cells were pre-incubated for 30 min with inhibitors and then cultured for 6 h in the presence of PACAP (10−7 M) or NGF (100 ng/ml). (A) Effect of protein kinase inhibitors on PACAP- and NGF-induced serpinb1a expression. Cells were pre-incubated with the PKA inhibitor H89 (10 µM), the PKC inhibitor Gö6983 (1 mM), or the PKA/PKC inhibitor H7 (50 µM). (B) Effect of TrkA and PI3K inhibitors on PACAP- and NGF-induced serpinb1a expression. Cells were pre-incubated with the TrkA inhibitor K252a (1 µM) or the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (20 µM). (C) Effect of MAP kinase inhibitors on PACAP- and NGF-induced serpinb1a expression. Cells were pre-incubated with the MEK inhibitors PD98059 (50 µM) or U0126 (25 µM), the p38 inhibitor SB203580 (10 µM), or the JNK inhibitor I (2 µM). (D) Effect of calcineurin inhibitors and calcium channel blockers on PACAP- and NGF-induced serpinb1a expression. Cells were pre-incubated with the calcineurin inhibitors ascomycin (100 nM) or cyclosporin A (100 nM), the FKBP12 inhibitor rapamycin (100 nM), or the calcium channel blocker D600 (30 µM). Quantitative PCR results were corrected using the GAPDH signal as internal control and expressed as the mean fold induction (± S.E.M.) of serpinb1a mRNA level compared to the control without inhibitor. ** p<0.01 versus control; # p<0.05 and ## p<0.01 versus PACAP without inhibitor; § p<0.05 and §§ p<0.01 versus NGF without inhibitor; NS, not significantly different from corresponding treatment without inhibitor.