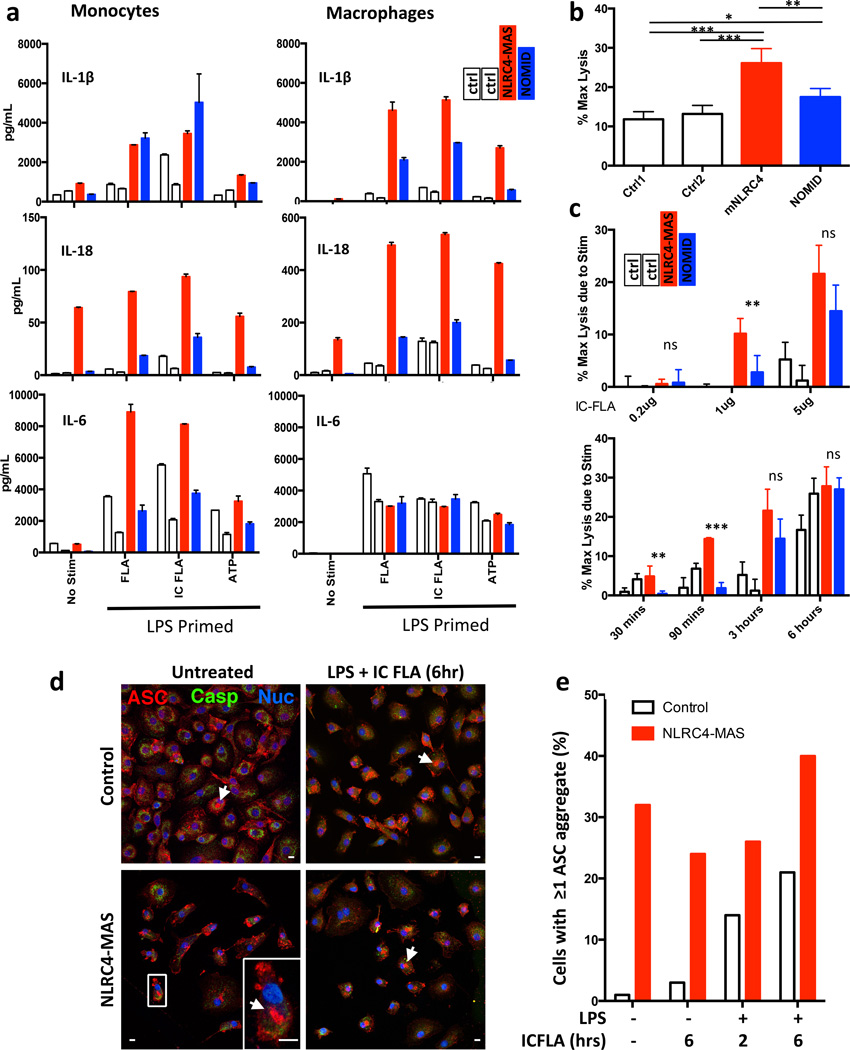
Figure 4. NLRC4-MAS monocytes and macrophages have increased inflammasome-related cytokine secretion, cell death, and ASC aggregate formation.
(a) Monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages from healthy controls (white bars) NLRC4-MAS (red) and NOMID patients (blue) were primed with LPS and stimulated with purified flagellin (FLA), liposomal flagellin (IC-FLA), or ATP. Secreted cytokines were measured by Luminex. Columns represent mean and SD of technical duplicates. Monocytes and macrophages represent matched samples. In LPS-primed cells, the addition of ATP did not alter cytokine production (data not shown). (b and c) LDH release as a marker of cell death, presented as the percentage of maximum lysis induced by 0.8% Triton X-100, was measured from macrophages after resting for six hours in serum-free medium alone (b) or after stimulation (c) with varying doses of IC-FLA for three hours (top) or with 5µg/mL IC-FLA for indicated time periods (bottom). Cell death assays were performed in biological quadruplicates. Mean and SD are representative of two independent experiments. Statistical comparisons were done by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s Post-test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.0001. Comparisons between NLRC4-MAS and NOMID are depicted. (d) and (e) Macrophages were stimulated as noted and imaged by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. Red staining represents ASC, Green indicates caspase-1, and blue indicates nuclei. Representative images (d) with a detail of a representative ASC aggregate (arrowheads and inset) were taken and ASC aggregate formation (e) was quantitated. A 10µm scale bar is shown. All samples from NLRC4-MAS and NOMID patients (a through e) were obtained after IL-1 receptor antagonist treatment for at least 3 months.