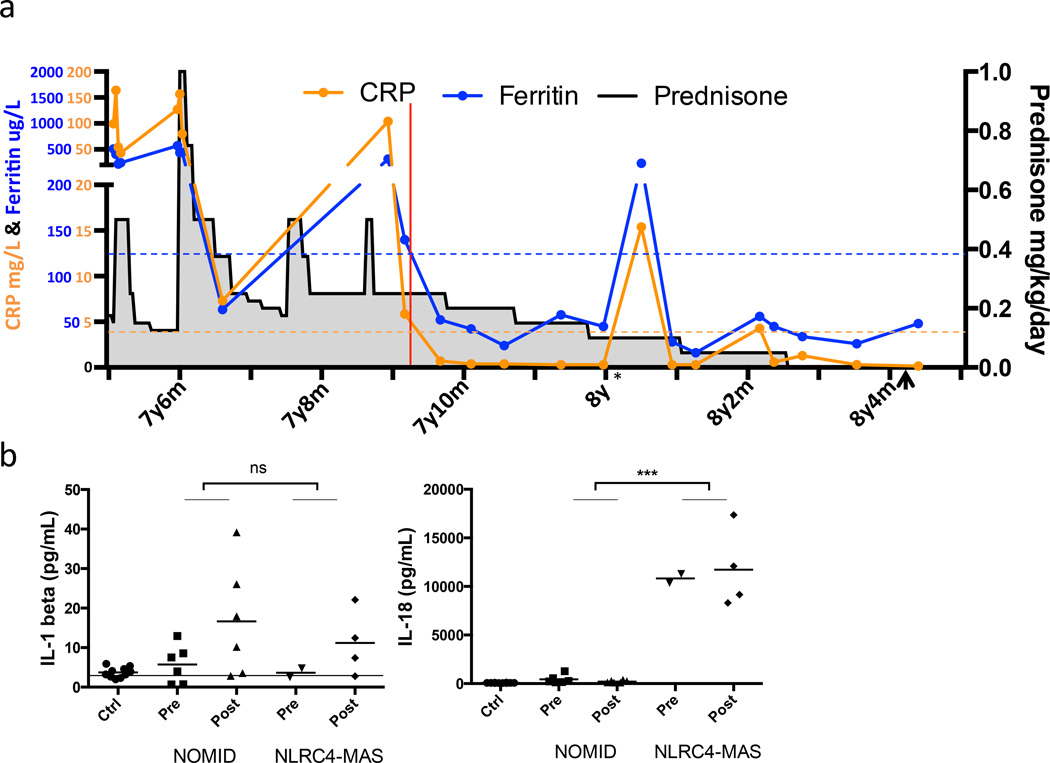
Figure 6. IL-1 receptor antagonist treatment normalized markers of systemic inflammation and enabled cessation of steroids, while serum IL-18 remained elevated.
(a) Chronologic depiction of C-reactive protein (CRP), serum ferritin, and prednisone dose before and after IL-1 receptor antagonist (anakinra) therapy. Red line indicates the start of anakinra treatment. Dashed lines represent the upper limits of normal. * Indicates a transient viral illness with temporary elevation of CRP and ferritin. Arrowhead indicates cessation of colchicine therapy. (b) Serum cytokines were assayed in the NLRC4-MAS patient, healthy pediatric controls, the patient’s family, and matched samples from six NOMID patients pre and post anakinra treatment. Control samples are grouped together. Horizontal line represents lower limit of detection. ***p<0.0001 for unpaired two-tailed student’s T-test of all NOMID patient samples versus all samples from NLRC4-MAS patient.