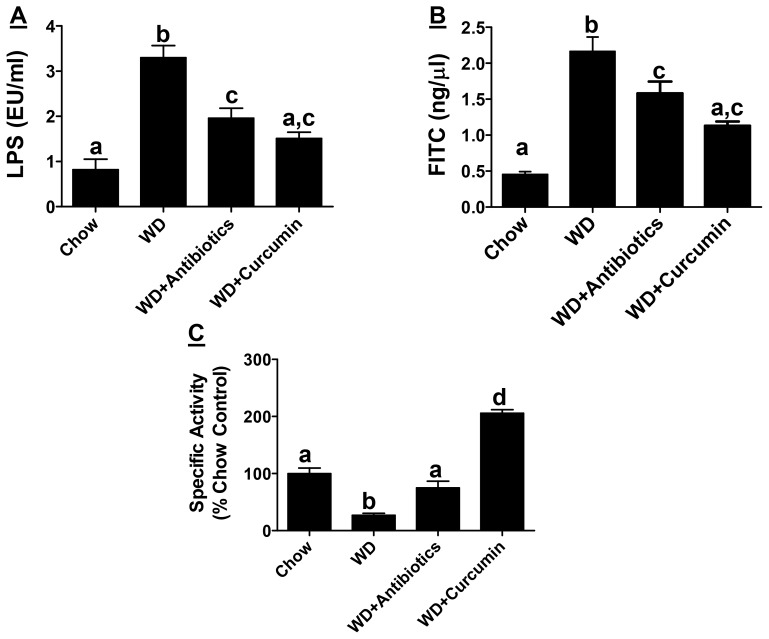
Figure 1. Supplementation with non-absorbable antibiotics or curcumin improves Western diet induced intestinal barrier dysfunction.
Ten week old LDLR−/− mice were fed ad libitum High Fat High Cholesterol containing Western type diet (TD 88137, WD) for 16 weeks. Experimental groups either received non-absorbable antibiotics (100 mg/L Neomycin and 10 mg/L Polymyxin B) in drinking water or were gavaged daily with Curcumin (100 mg/kg in 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose). Panel A: Fasting plasma was collected at the time of necropsy and circulating LPS levels (EU/ml) were determined. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM, n = 6–9 per group. Panel B: Overnight fasted mice were gavaged with FITC-dextran 4 kDa and plasma samples were collected after 4 h. Appearance of FITC-dextran in plasma was monitored and the data (Mean±SEM, n = 6–9, per group) are presented as FITC concentration (ng/µl). Panel C: Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase activity was determined and Specific activity (nmoles PNP released/h/mg protein) expressed as % chow-fed controls is shown (Mean ± SEM, n = 6–9 per group). P<0.0001 by One way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc correction; Dissimilar letters above the bars indicate significant differences between groups (P<0.05).