Fig. 1.
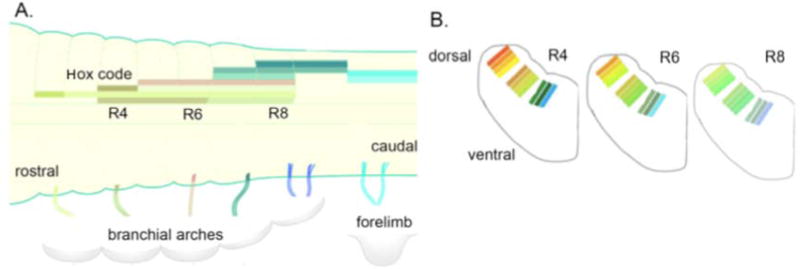
A. Hindbrain rhombomeres are specified from anterior to posterior by a Hox code; here each Hox gene is indicated by a different pastel-colored bar (note that the code can be combinatorial). Hox genes are a sub-set of homeotic genes implicated in segmental identities. The branchial arches and forelimbs are innervated by neurons whose axons form the caudal cranial nerves. Based on [17]. B. Transverse sections through the hindbrain at levels from R4 to R8. Groups of interneurons are organized in stripes (indicated by brightly colored bars; these do not match part A) and can be identified by expression of transcription factors and genes associated with neurotransmitter identity (modified from[16]). Abbreviation: R, rhombomere.
