Fig. 2.
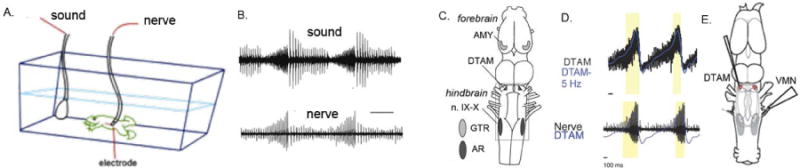
A. and B. An underwater microphone records advertisement calling in a male X. laevis and an en passant electrode records vocal nerve activity (compound action potentials) [32]. C. Components of the neural pathway for call production in X. laevis. The hindbrain VPG includes nucleus DTAM rostrally and interneurons at the anterior pole of nucleus (n.) IX–X caudally. DTAM and vocal motor neurons express androgen receptor (AR). In the forebrain, the amygdala (AMY) expresses receptor for gonadotropin (GTR) and projects to DTAM. Modified from [54]. D. Recordings of a local field potential (highlighted in yellow) from DTAM in the isolated brain (in blue) reveal activity that mirrors the fictive advertisement call pattern recorded from the vocal nerve (lower panel; figure by C. Barkan). Abbreviations: AMY, amygdala; DTAM, used as a proper noun; n. IX–X, nucleus ambiguus, VMN, vocal motor nerve.
