Figure 2.
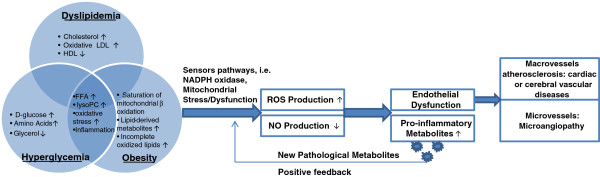
Metabolome analysis related to hyperglycemia/insulin resistance, obesity, and hyperlipidemia which contribute to the development of endothelial dysfunction. The reciprocal effects of hyperglycemia/insulin resistance, obesity, and dyslipidemia result in mitochondria stress/dysfunction via a complex of factors including oxidative stress, inflammation, incomplete fat oxidation, etc. As a result, mitochondria dysfunction increases the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and decreases nitric oxide (NO), which ultimately produces endothelial dysfunction and progressively causes atherosclerosis in macrovessels and microangiopathy in microvessels.
