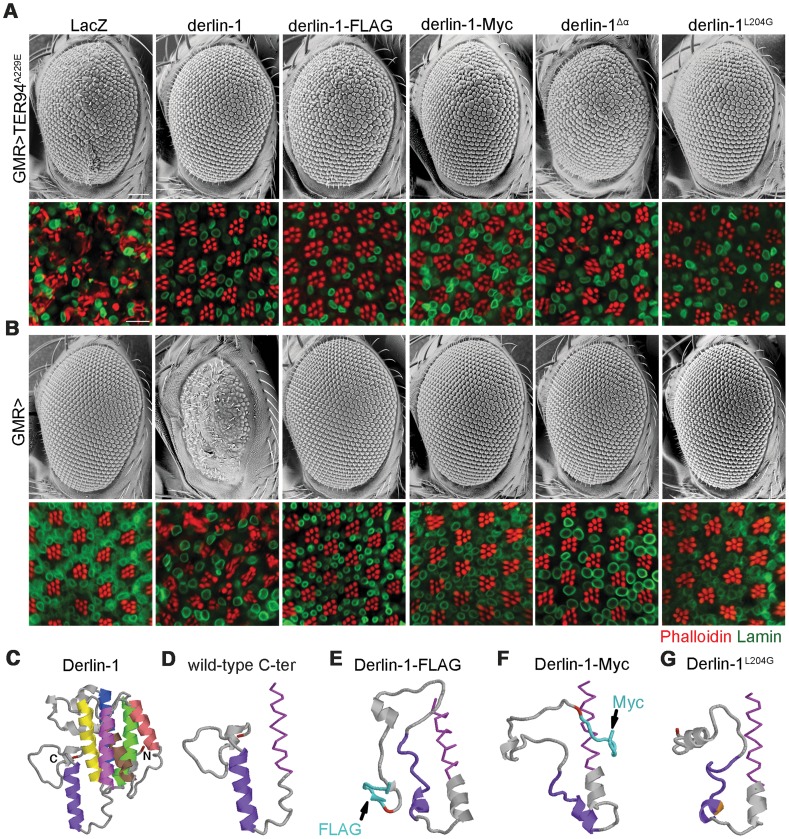
Figure 10. The C-terminal α-domain is required for Derlin-1 overexpression-induced cytotoxicity.
(A and B) SEM (upper row) and confocal section (lower row) of 1-day-old adult fly eyes expressing the indicated transgenes with (A) or without (B) TER94A229E using GMR-GAL4 driver. Phalloidin (red) and anti-Lamin antibodies (green) are used to label the rhabdomeres and the nuclear envelopes, respectively. Scale bars: 100 µm (SEM), 10 µm (confocal). (C–G) Structural prediction of Derlin-1 constructs by I-TASSER. (C) Full-length Derlin-1 features six major helixes (colored in blue, green, yellow, brown, red, and magenta from first to sixth helix), corresponding to the transmembrane domain. The C-terminal cytoplasmic tail contains the seventh helix (colored in purple). (D–G) The predicted sixth (magenta) transmembrane helix (shown as sticks view) and the C-terminal cytoplasmic tail (shown as cartoon view) of wild-type Derlin-1 (D), FLAG-tagged Derlin-1 (E), Myc-tagged Derlin-1 (F), and Derlin-1L204G (G). The last residue of Derlin-1 is marked in red. Epitope tags and altered residue are marked in cyan (E and F) and gold (G), respectively.