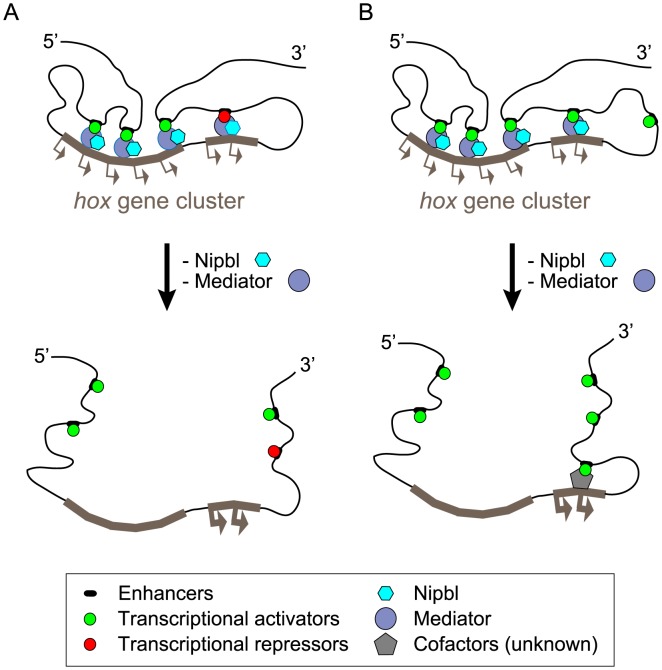
Figure 10. Model of hox gene regulation by Nipbls and mediator.
Along topological domains, 3′- and 5′-hox genes tend to interact with limb-specific regulatory elements in telomeric and centromeric landscapes, respectively. These interactions are required to establish proper patterns of hox gene expression in limb/fin buds and depend on Nipbl/Mediator. The long-range enhancer-promoter interactions are disrupted in the absence of Nipbl and Med12, leading to dysregulation of hox genes. (A) Expanded expression of 3′ -hox genes might be allowed when released from putative remote repressors in Nipbl/Med12-deficient fin buds. (B) Alternatively, disruption of chromosomal conformation may lead to replacement of 3′ remote enhancers with (more closely located) putative ectopic enhancers that can activate 3′-hox genes strongly through long-range interactions.