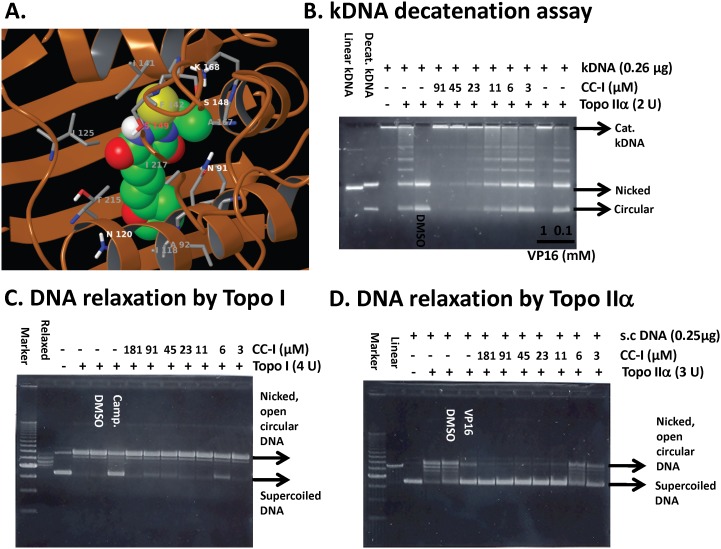
Figure 6. Topoisomerase IIα inhibition by CC-I.
(A) Structure of CC-I docked into topoisomerase IIα (pdb code 1ZXM). Topoisomerase is shown as the brown-colored ribbon with residues on the binding site. Carbon atoms of CC-I are colored green, while those of topoisomerase is colored gray. Other atoms are colored according to atom types, i.e., nitrogen-blue, oxygen-red, sulfur-yellow, and polar hydrogen white. Non-polar hydrogen atoms are not shown. (B) The CC-I concentration-dependent inhibition of human topoisomerase IIα-mediated kDNA decatenation. All experiments were carried out according to instructions from the Topogen kit (Port Orange, FL). Reactions contained 4U of enzyme, 0.26 µg of DNA substrate, and different concentrations of the CC-I dissolved in DMSO (0.5% final concentration (v/v)). Different topological forms exhibited different mobility as indicated. Linear, linear kDNA; Decat., decatenated kDNA; Nicked, nicked decatenated kDNA; circular, circular decatenated kDNA; kDNA, kinetoplast DNA. VP16 was used as a positive control. (C) CC-I did not inhibit topo-I mediated supercoiled pHOT1 DNA relaxation. The procedures are described in method section. Camptothecin (camp.) was used as a positive control. (D) CC-I dose dependently inhibited topoisomerase IIα-mediated supercoiled pHOT1 DNA relaxation. VP16 was used as a positive control. s.c. DNA, super-coiled DNA.