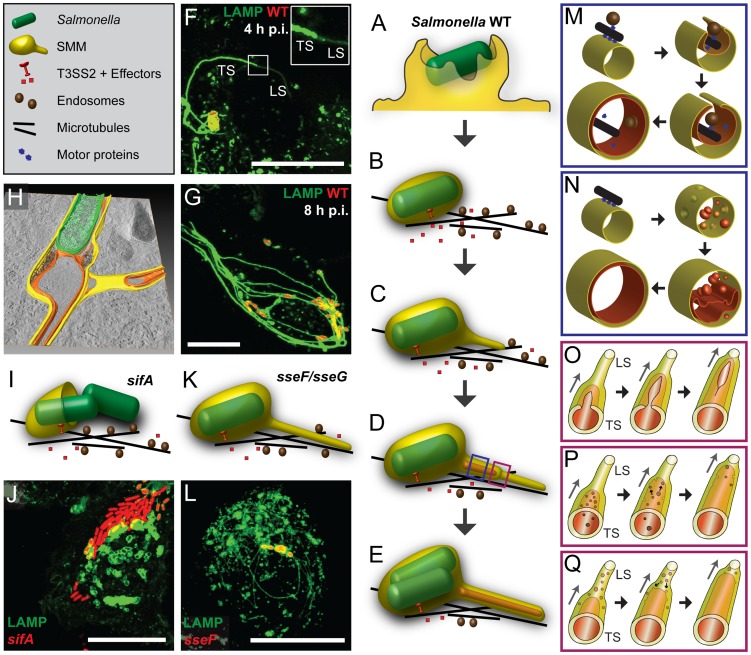
Figure 11. Models for the biogenesis of SIF.
Schematic depiction of events leading to engulfment of cytosol and cytoskeletal elements, and formation of double membrane structures. After invasion of host cells by Salmonella involving ruffle formation (A), the internalized pathogen is located in a host-derived membrane compartment, called Salmonella-containing vacuole (SCV) that moves along microtubules (B) towards the MTOC. Subsequently, Salmonella activates the SPI2-T3SS and translocation of effector proteins into the host cytosol, thereby starting the induction of SIF. These tubular structures are formed through fusion processes with endosomes that move along microtubules (MT). In the initial phase (3–4 h p.i.) SIF consist only of one membrane (C) that undergo a process resulting in SIT consisting of double membranes (D, E). In the initial phase of centrifugal extension of SIT (D, F), we observed thinner single membrane SIF at the tips (leading SIF, LS) and thicker double membrane SIF at the base (trailing SIF, TS). At later time points (8–10 h p.i.) a stable double membrane SIF network is induced by Salmonella WT, accompanied by a strong reduction of host cell endosomes (E, G). The tomogram of a Salmonella WT-infected cell indicates the features of SCV and double membrane SIT (H). The sifA mutant strain is not capable of maintaining the membrane integrity of the SCV, Salmonella escape from the damaged SCV into the cytoplasm and no SIF formation is observed (I, J). The sseF and sseG mutant strains induce thin SIF consisting of one membrane (K, L). M) and N) show scenarios for conversion of single to double membrane SIF (blue boxes). M) Tubular membranes are formed along MT. By lateral extension, these membranes enwrap the guiding MT, as well as vesicles transported along MT and portions of cytoplasm. Membrane fusions results in formation of double membrane SIF. N) Alternatively, membrane invagination generates small vesicles that accumulate within single membrane SIF and the fusion of these vesicles results in formation of inner membrane tubule and its continuous extension. In both models, the lumen of the inner tubule is segregated from Salmonella. O), P), Q) Models for the dynamic conversion of LS to TS (red boxes). See main text for further details. Scale bars: 20 µm.