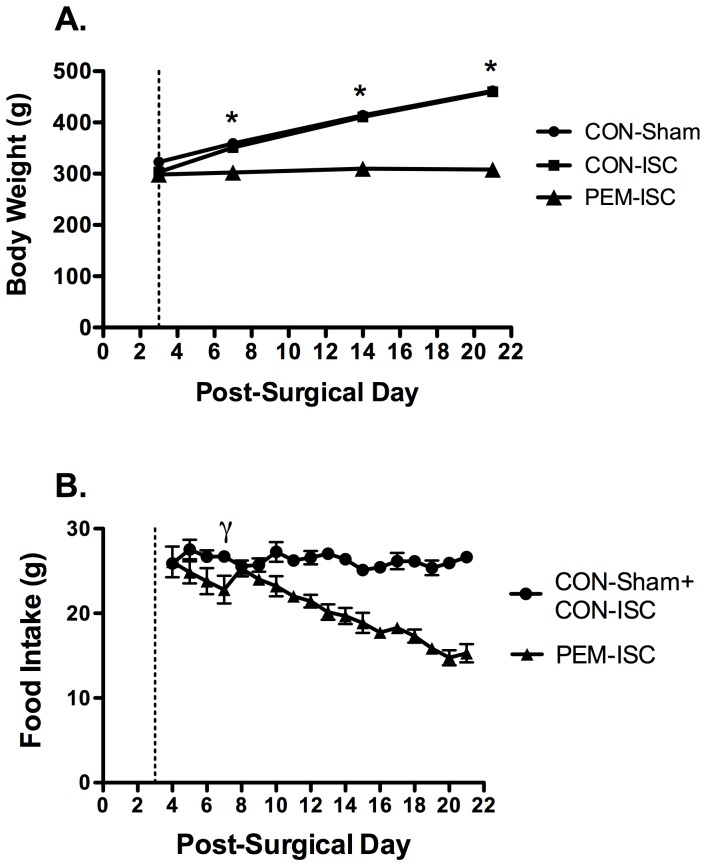
Figure 1. The PEM regimen introduced on day 3 after global brain ischemia depressed body weight and food intake.
Data are shown as mean ± SEM for the day 21 treatment groups. The dashed vertical line illustrates the day on which rats were assigned to experimental diet. (A) Body weights are shown for days 3, 7, 14 and 21 (CON-Sham21d, n = 8; CON-ISC21d, n = 11; PEM-ISC21d, n = 11).*Indicates a significant effect of experimental diet on body weight (PEM-ISC compared to CON-Sham and CON-ISC groups) by Tukey's Test (p<0.05). (B) Food intake was collected daily on a cage basis (CON-Sham21d + CON-ISC21d, n = 8 cages [2–3 rats/cage]; PEM-ISC21d, n = 5 cages [2–3 rats/cage]) and calculated as daily cage food intake/number of rats per cage. γ Indicates the first day on which PEM-ISC rats experienced a significant reduction in food intake, when compared to that for the combined CON groups, as detected by an independent-sample Student's t-test (p<0.05).