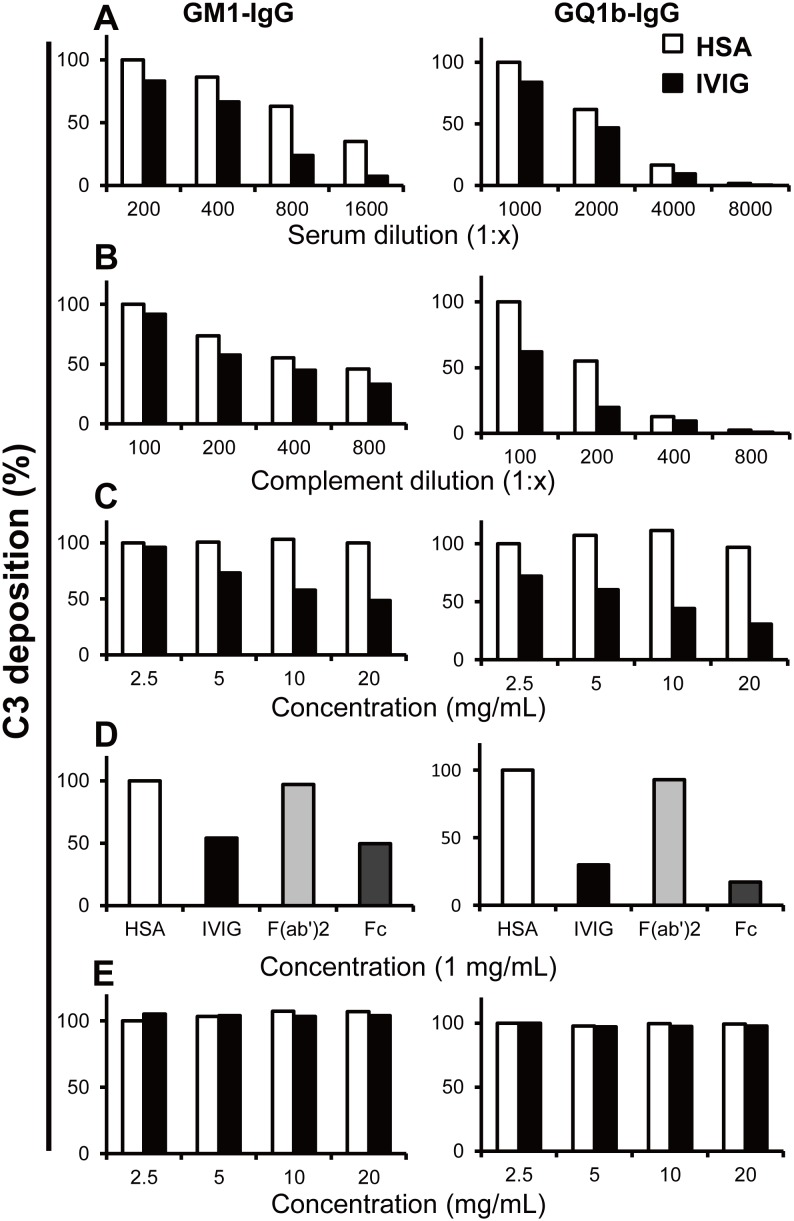
Figure 3. Complement deposition on ganglioside-coated microtiter plates using serum anti-GM1 or anti-GQ1b IgG antibodies from patients with Guillain–Barré or Miller Fisher syndrome.
Reduction of C3 deposition in the presence of constant amounts of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) (10 mg/mL) or human serum albumin (HSA, 10 mg/mL; control) and serial dilution of patients’ serum (A) or complement source (B). C3 deposition decreased along with serial dilution of patients’ serum and complement source. Dose-dependent inhibition of C3 deposition by IVIG compared with HSA (C). F(ab’)2 did not inhibit C3 deposition whereas IVIG and the Fc portion did (1 mg/mL) (D). Antibodies once bound to GM1 or GQ1b were not displaced by IVIG (E). Results were given as optical densities (OD) at 492 nm. The results were normalized to the lowest concentration of HSA treated, and showed as % of control. Each experiment was performed at least 3 times for each serum sample with anti-GM1 (n = 3) and anti-GQ1b IgG antibodies (n = 3) and representative results were shown. Experiment condition: (A) complement source (1∶100); (B) serum sample with anti-GM1 (1∶200), anti-GQ1b (1∶1000) IgG antibodies; (C–E) serum sample with anti-GM1 (1∶200), anti-GQ1b (1∶1000) IgG antibodies, complement source (1∶100).