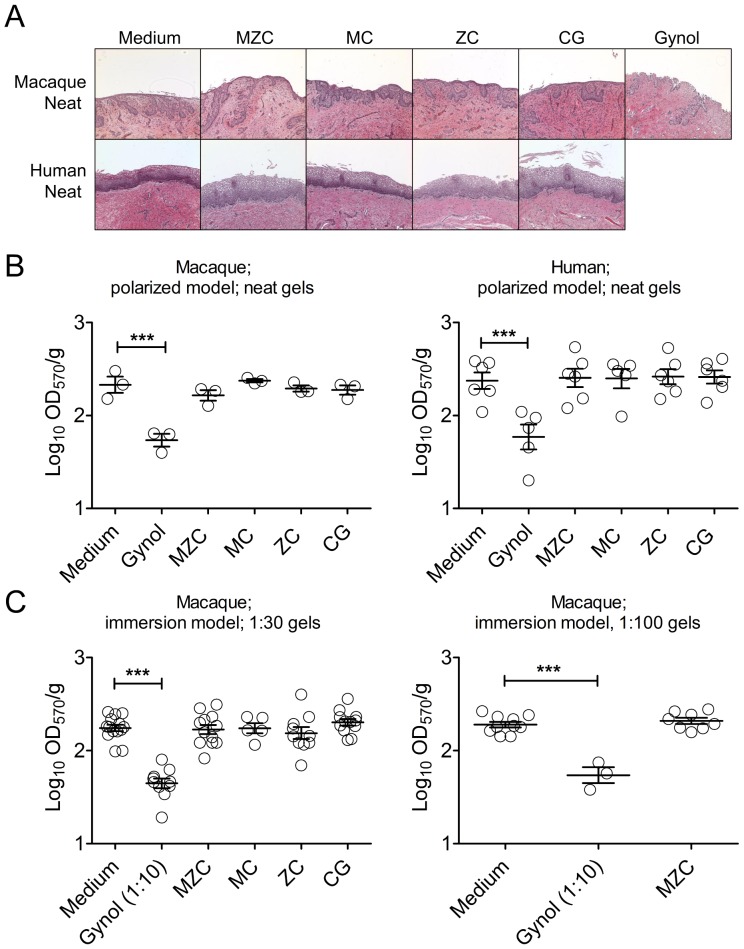
Figure 2. MZC is not toxic in macaque vaginal and human ectocervical explants.
(A) Polarized macaque vaginal and human ectocervical explants were cultured for ∼18 h in the presence of neat modified gels, applied on the epithelium. For histological evaluation, after exposure to MZC, MC, and ZC, or control conditions (medium, CG, Gynol), tissues were washed, paraffin-embedded, and stained with H&E. Results representative of 4–6 (macaque) and 1–2 (human) experiments are shown at 10× magnification. (B) For determination of tissue viability polarized macaque vaginal and human ectocervical explants (single tissues) were incubated with neat modified MZC, MC, ZC (vs. Medium, CG and Gynol controls) applied on the epithelium for ∼18 h. Each symbol indicates a donor and the Mean±SEM of the log10(OD570/g) for each condition is shown. (C) Macaque vaginal explants (2–4 per condition) were immersed in culture media with diluted (1∶30 or 1∶100) modified gels (vs. Medium and 1∶10 diluted Gynol control) for ∼18 h. Following incubation with the gels, tissue viability was determined using MTT assay. Each symbol indicates a donor and the Mean±SEM of the log10(OD570/g) for each condition is shown.