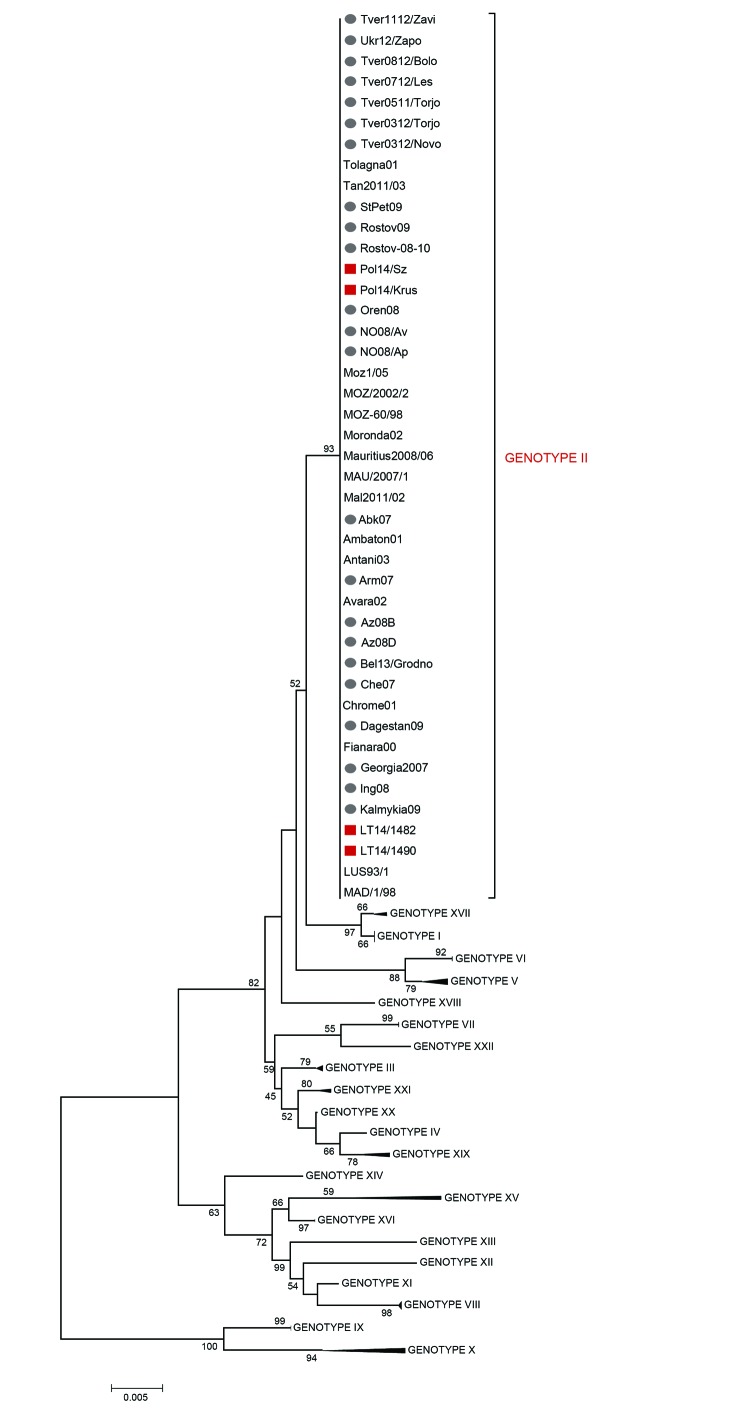
Figure 2.
Minimum evolution (ME) phylogenetic tree of African swine fever virus (ASFV) isolates from Lithuania and Poland based on the C-terminal end of the p72 coding gene relative to the 22 p72 genotypes (labeled I-XXII), including 88 nt sequences. The tree was inferred by using the ME method (http://www.megasoftware.net/mega4/WebHelp/part_iv___evolutionary_analysis/constructing_phylogenetic_trees/minimum_evolution_method/rh_minimum_evolution.htm) following initial application of a neighbor-joining algorithm. The phylogenetic tree was rooted by the midpoint method. The percentage of replicate trees >50% in which the associated taxa clustered together by bootstrap analysis (1,000 replicates) is shown adjacent to the nodes. The robustness of the ME tree was tested by using the close-neighbor-interchange algorithm at a search level of 1. Squares indicate ASFV isolates from Lithuania and Poland that were genotyped in this study; circles indicate ASFV isolates during 2007–2013 from the Caucasus region. Scale bar indicates nucleotide mutations per site.