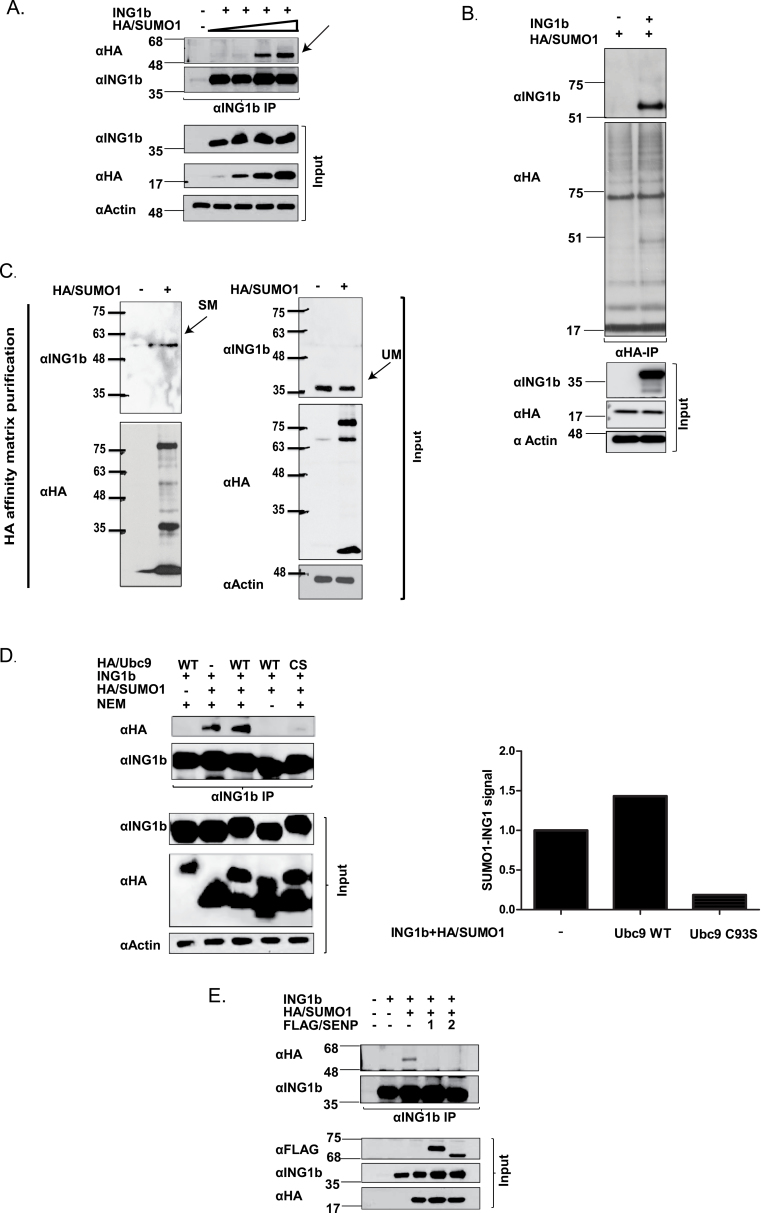
Fig. 1.
ING1b is SUMOylated. (A) ING1b expression construct was cotransfected with increasing concentrations of HA/SUMO1 expression construct in HEK293 cells. Cells were lysed in the presence of N-ethylmaleimide and lysates were subjected to denaturing αING1 IP and IB with SUMO1 (αHA) and ING1 (Cab1 and Cab5) to detect SUMOylated and unSUMOylated ING1b. (B) U20S cell lysates expressing HA/SUMO1 with or without ING1b were subjected to αHA IP and IB with HA and ING1 antibodies. (C) U2OS cell lysates with or without HA/SUMO1 was subjected to anti-HA purification using HA affinity matrix under denaturing conditions. SDS-Laemmli sample buffer (2×) was used to elute the SUMOylated proteins and eluent was subjected to SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis electrophoresis. αING1 IBs were performed to detect endogenous SUMOylated ING1b protein followed by αHA to detect purified SUMOylated proteins. αING1 and αHA (SUMO1) and α-actin IB were performed to confirm protein expression and equal loading, respectively. Black arrows depicting SM (sumoylated) and UM (unmodified) denotes SUMO-modified ING1b and unmodified ING1b, respectively. Major SUMOylated endogenous protein species of ~68 and ~85kDa were visualized in the input lysate, whereas a protein of ~85kDa was recovered from the HA affinity matrix. The band at ~20kDa could be free SUMO1. (D) HEK293 cells expressing HA/Ubc9 WT or HA/Ubc9 CS were immunoprecipitated with αING1 followed by IB with αHA and αING1 to detect SUMOylated ING1b, HA/SUMO1, HA/Ubc9 and modified and unmodified ING1, respectively. The associated graph indicates the relative density of SUMOylated ING1b in cells expressing Ubc9 WT or Ubc9 CS mutant. (E) HEK293 cells expressing ING1b and HA/SUMO1 were coexpressed with FLAG-tagged SENP1 or SENP2 and levels of SUMOylated ING1b were assessed by denaturing IP of ING1b and IB against αHA-SUMO. Expression of the different transfected constructs was checked with αFLAG (SENP1 and 2), αHA (SUMO1) and αING1.