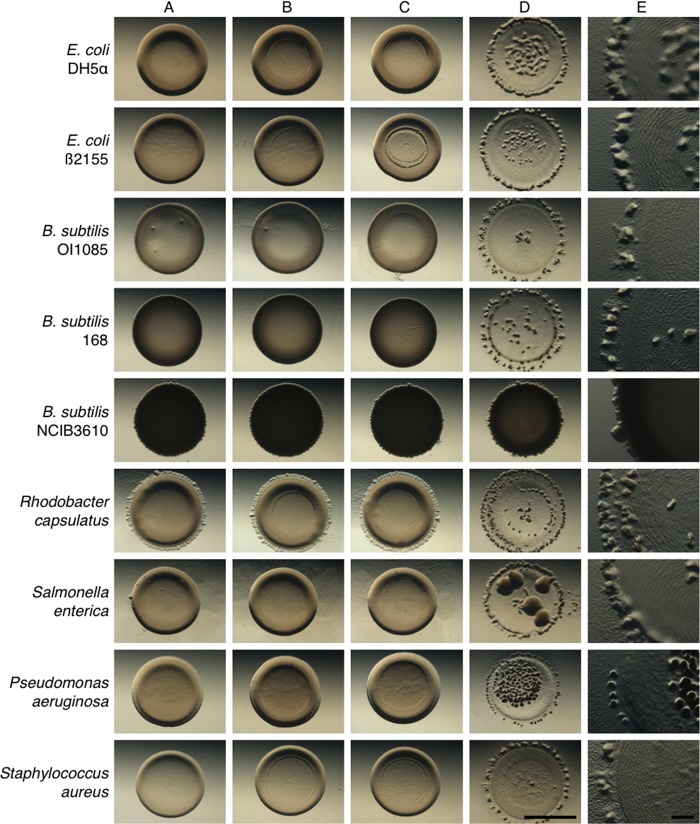
FIG 1.
M. xanthus predation of various prey strains. Shown are predation assays using different Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains as prey for M. xanthus predator cells. Efficient predation results in clearing of the prey spot, with M. xanthus fruiting body formation occurring at the edge of the original prey spot. The prey strains tested were E. coli DH5α and B2155, B. subtilis OI1085, 168, and NCIB3610, Rhodobacter capsulatus, Salmonella enterica, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus. Strains resisting predation show only minimal lysis at the center of the prey spot. (A) Prey only; (B) prey with buffer spotted at center; (C) prey with heat-killed predator; (D) prey with predator. Pictures were taken at 48 h after spotting at a magnification of ×10 (A to D) or ×30 (E). Bars, 0.5 cm (A to D) and 0.1 cm (E).