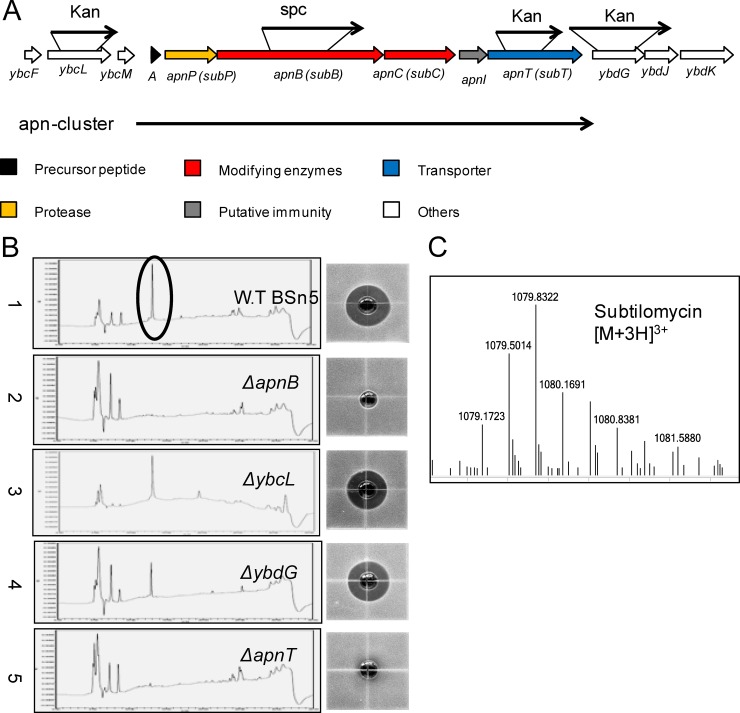
FIG 2.
The subtilomycin gene cluster and inactivation analysis of related genes. (A) The apn cluster genes are shown in different colors: the precursor peptide encoded by apnA is shown in black, the genes encoding modifying enzymes are shown in red, the gene encoding protease is shown in yellow, the gene involved in putative immunity is shown in gray, and the gene encoding the transporter is shown in blue. The flanking genes are shown in white and are numbered. The black arrow indicates related genes interrupted by spectinomycin (Spc) or kanamycin (Kan) resistance genes. (B) Bioassay and high-performance liquid chromatography results for detection of subtilomycin from active ammonium sulfate crude extracts of wild-type strain BSn5 and its mutants. 1, wild-type strain BSn5; 2, ΔapnB mutant; 3, ΔybcL mutant; 4, ΔybdG mutant; 5, ΔapnT mutant. The black ring refers to the respective target peaks of subtilomycin in high-performance liquid chromatography. (C) ESI-MS detection of subtilomycin production in the 12-h supernatant of the recombinant harboring the apn cluster. The triply charged ion [M + 3H]3+ is shown.