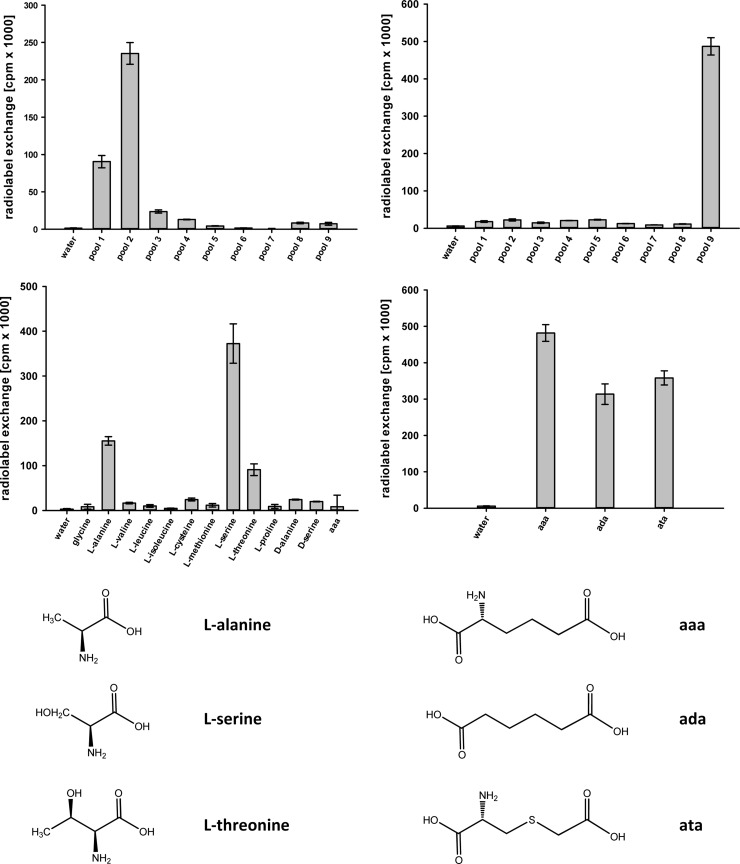
FIG 3.
Substrate specificity of C. subvermispora reductases Nps1 (left) and Nps3 (right) based on the substrate-dependent ATP-[32P]pyrophosphate exchange assay. Diagrams represent assays with pools of substrates (top) and individual compounds (bottom). Error bars indicate the standard deviations. Composition of pools was as follows: pool 1, Gly, l-Ala, l-Val, l-Leu, l-Ile; pool 2, l-Cys, l-Met, l-Ser, l-Thr, l-Pro; pool 3, l-His, l-Phe, l-Tyr, l-Trp; pool 4, l-Asp, l-Asn, l-Glu, l-Gln; pool 5, l-Lys, l-Arg, l-Orn, oxalic acid; pool 6, pyruvic acid, α-ketoglutaric acid, phenylpyruvic acid, 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid, indole-3-pyruvic acid; pool 7, malonic acid, succinic acid, fumaric acid, maleic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid; pool 8, benzoic acid, salicylic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid. aaa, l-α-aminoadipic acid; ada, adipic acid; ata, l-α-amino-4-thia-adipic acid.