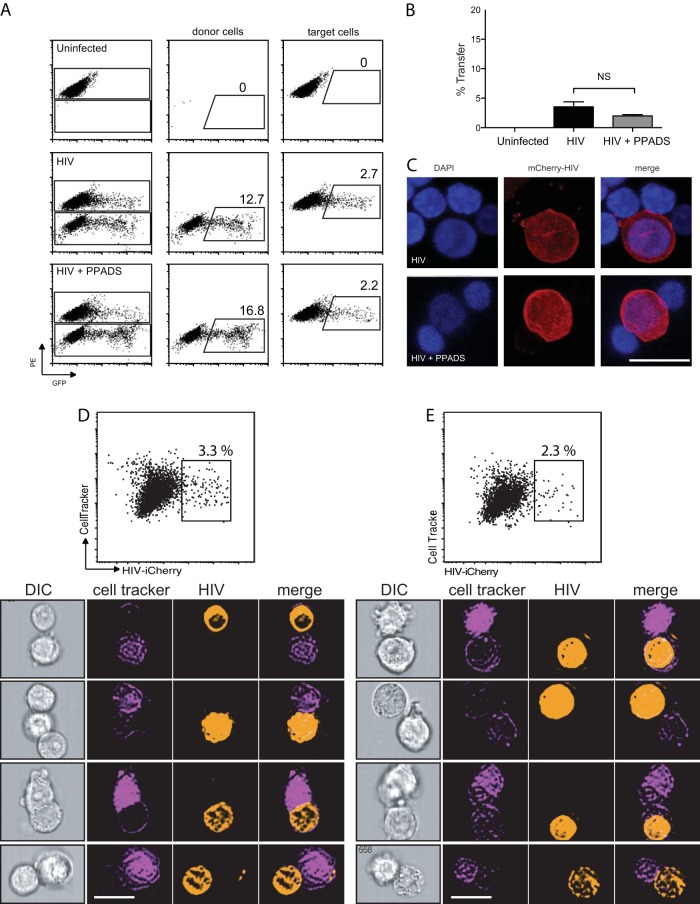
FIG 2.
PPADS does not inhibit cell-to-cell transfer of HIV. Jurkat cells were transfected with HIV-1 Gag-iGFP. Target primary CD4+ T cells were stained, and both donor and target cells were preincubated with inhibitor for 30 min prior to mixing. Cells were coincubated for 4 h and then fixed and analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorter plots of uninfected target cells (top), cells infected with Gag-iGFP (middle), and cells infected with Gag-iGFP in the presence of 100 μM PPADS (bottom). (B) Quantification of transfer efficiency from flow cytometry of uninfected target cells, cells infected with Gag-iGFP, and cells infected in the presence of 100 μM PPADS. Results are the means ± SEMs of three independent experiments. NS, nonsignificant. (C) Confocal micrographs of infected Jurkat cells associated with target primary CD4+ T cells. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole), and HIV (mCherry-HIV) is in red. Bar, 10 μm. (D, E) Flow cytometric imaging was performed on cells infected with Gag-iGFP (D) or infected in the presence of 100 μM PPADS (E) after incubation for 4 h. (Top) Representative plots of the cells are shown (results are the means ± SEMs of three independent experiments); (bottom) examples of cells identified by flow cytometry imaging are shown below for each condition. Stable associations of donor and target cells were identified as follows: cells were sorted for doublets in which a single cell stained positive for CellTracker (target cells) and the second cell stained positive for iCherry (donor). Bars, 10 μm. DIC, differential interference contrast.