FIG 1.
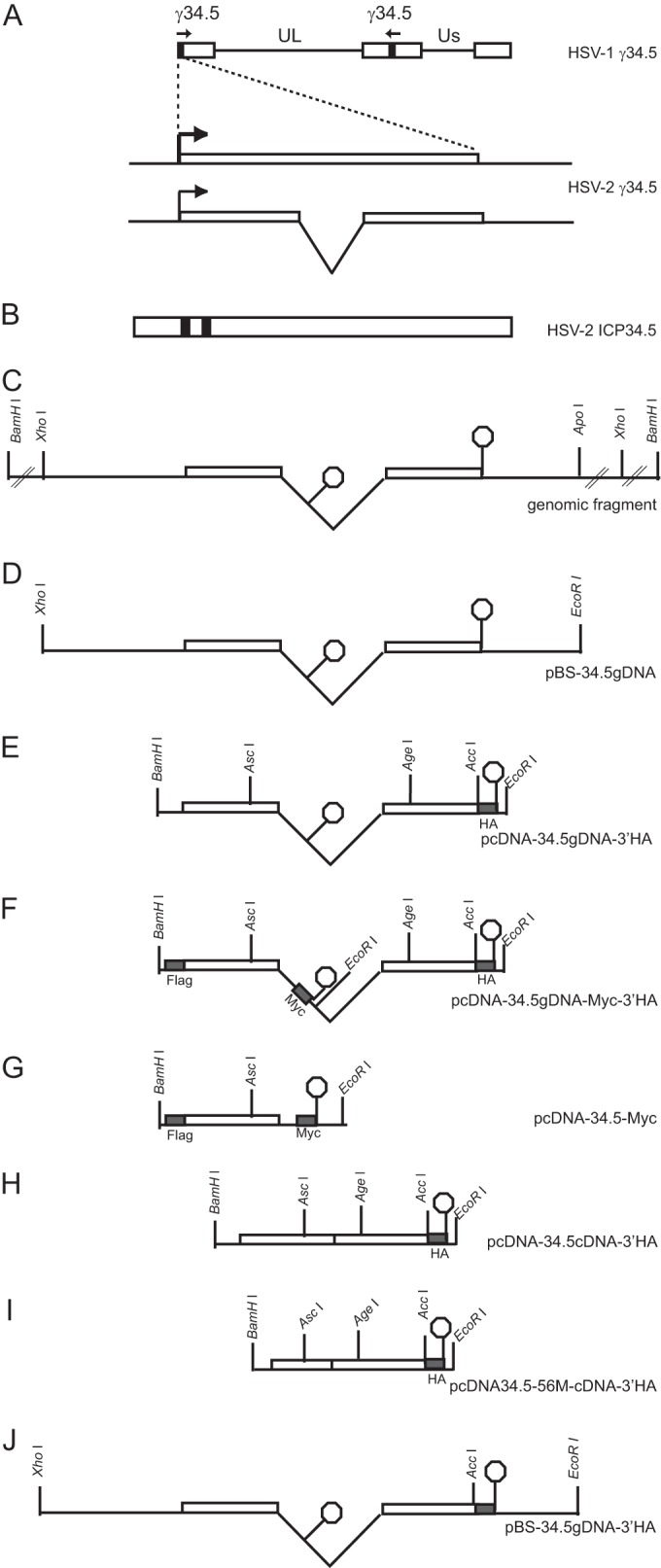
HSV-1 and HSV-2 γ34.5 open reading frames and expression constructs generated. (A) Two copies of the γ34.5 gene are located in the repeat regions of the HSV-1 and HSV-2 genomes. The HSV-1 γ34.5 gene consists of a single exon, and the HSV-2 γ34.5 gene contains an intron. Us, unique short region; UL, unique long region. (B) The HSV-2 ICP34.5 polypeptide translated from the mature spliced γ34.5 mRNA, with locations of peptide epitopes (solid boxes) used to generate rabbit antiserum. (C) BamHI genomic fragment of HSV-2 333 DNA containing the γ34.5 gene. (D) HSV-2 γ34.5 gene subcloned into pBS(+). (E) HSV-2 γ34.5 gene subcloned into pcDNA3.1(+) and fused in frame with a 3′ HA tag. (F) 34.5gDNA-3′HA construct mutated to encode Flag and Myc tags. (G) 34.5gDNA-Myc-3′HA construct truncated after the Myc tag. (H) 34.5cDNA construct with 3′ HA tag. A vertical line indicates the exon boundary. (I) Example of an N-terminal truncation mutant constructed from the cDNA plasmid. (J) Plasmid containing the HSV-2 γ34.5 gene with a 3′ HA tag used to produce the recombinant HSV-2 strain 34.5gDNA-3′HA.
