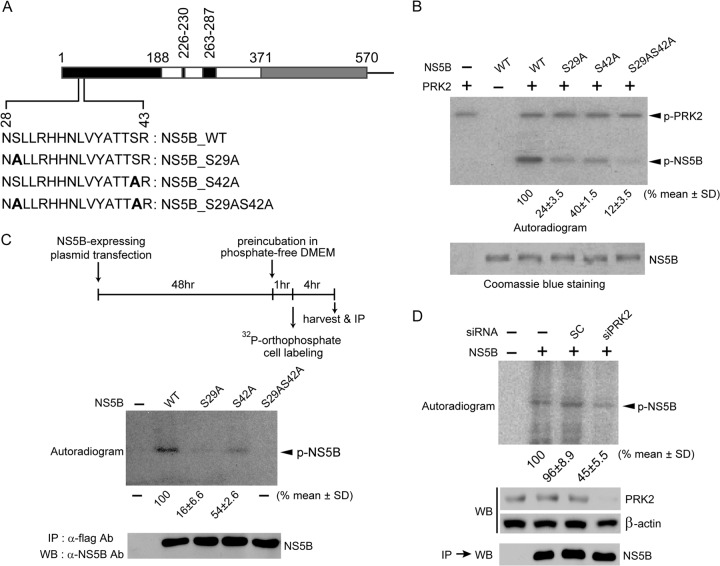
FIG 4.
The Ser29 and Ser42 residues of HCV NS5B are its two major phosphorylation sites. (A) The HCV NS5B protein (570 amino acids [aa]) lacking 21 C-terminal hydrophobic amino acids is illustrated schematically. The region containing the two phosphorylation sites (Ser29 and Ser42) is expanded below the schematic to show the substituted amino acids (boldface) used in the in vitro kinase assays. (B) In vitro kinase assays were performed with wild-type (WT) NS5B and the indicated NS5B mutants as for Fig. 2B. The bottom gel shows equivalent amounts of NS5B used for the assays. Phosphorylated, radiolabeled NS5B signals were quantified using a phosphorimager and normalized to NS5B protein levels. The results shown below the autoradiogram represent the means ± standard deviations (SD) of three experiments, from which one representative autoradiogram is shown. (C) Huh7 cells transfected with plasmids expressing the indicated NS5B proteins were metabolically labeled with [32P]orthophosphate. The labeled NS5B proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP), resolved by SDS-PAGE, and analyzed by autoradiography (top) or Western blot analysis (bottom). Phosphorylated-NS5B levels were quantified as for panel B. (D) Experiments similar to those shown in panel C were performed with or without silencing of PRK2 expression. Knockdown of PRK2 in cells transfected with siPRK2 was verified by Western blotting.