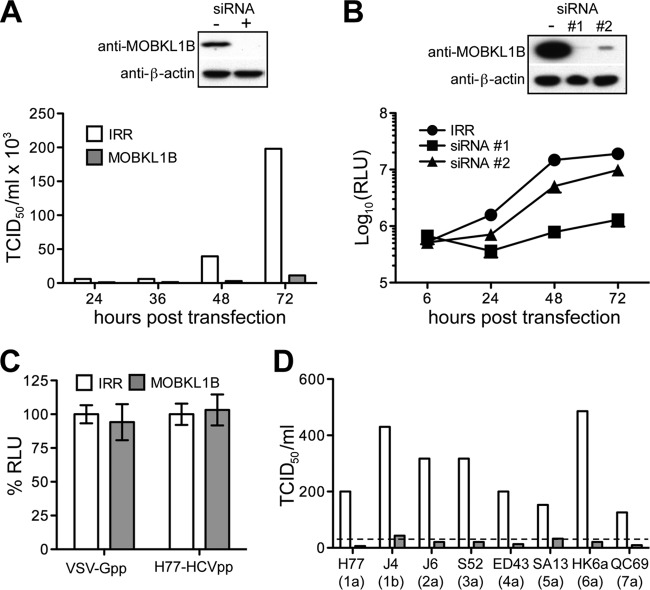
FIG 2.
Treatment with MOBKL1B siRNA inhibits HCV RNA replication. (A) HCV growth in culture is inhibited by MOBKL1B depletion. Huh-7.5 cells were transfected twice with MOBKL1B-specific or irrelevant (IRR) siRNA at 24-h intervals and were infected with HCV Jc1 at 48 h after the second transfection. Depletion of endogenous MOBKL1B protein was analyzed by Western blotting (top panel); β actin levels are shown as a control. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (B) MOBKL1B depletion blocks viral RNA replication. Depletion of MOBKL1B in CD81 knockdown Huh-7.5 cells was performed, as described above. Two individual MOBKL1B-specific siRNAs (1 and 2) were used. Jc1FLAG(p7-nsGluc2A) RNA was transfected at 48 h after the second siRNA transfection. At each indicated time point, released luciferase was measured to analyze viral RNA replication (mean of n = 3; error bars, SD). RLU, relative light units. (C) MOBKL1B knockdown does not affect the entry of pseudoparticles. After siRNA 1 treatment, Huh-7.5 cells were infected with luciferase reporter pseudoparticles at 48 h after the second siRNA transfection. Luciferase was measured at 48 h after infection. Values are normalized to RLU measured in irrelevant-siRNA-treated cells (mean of n = 3; error bars, SD). VSV-G, vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein; H77-HCV, HCV strain H77 glycoproteins. (D) MOBKL1B is also required for the replication of J6/JFH1-based HCV NS5A recombinants. MOBKL1B depletion and viral genome transfection were performed as described above. Recombinant HCV variants were as follows: 1a, J6/JFH1(H77-NS5A); 1b, J6/JFH1(J4-NS5A)R867H, C1185S; 2a, J6/JFH1(J6-NS5A)F772S; 3a, J6/JFH1(S52-NS5A)D1975G; 4a, J6/JFH1(ED43-NS5A)F772S, Y1644H, E2267G; 5a, J6/JFH1(SA13-NS5A)R1978G, S2416G; 6a, J6/JFH1(HK6a-NS5A)I2268N; 7a, J6/JFH1(QC69-NS5A). The results shown are representative of two independent experiments. The dashed line indicates the quantitation limit of the assay.