FIG 7.
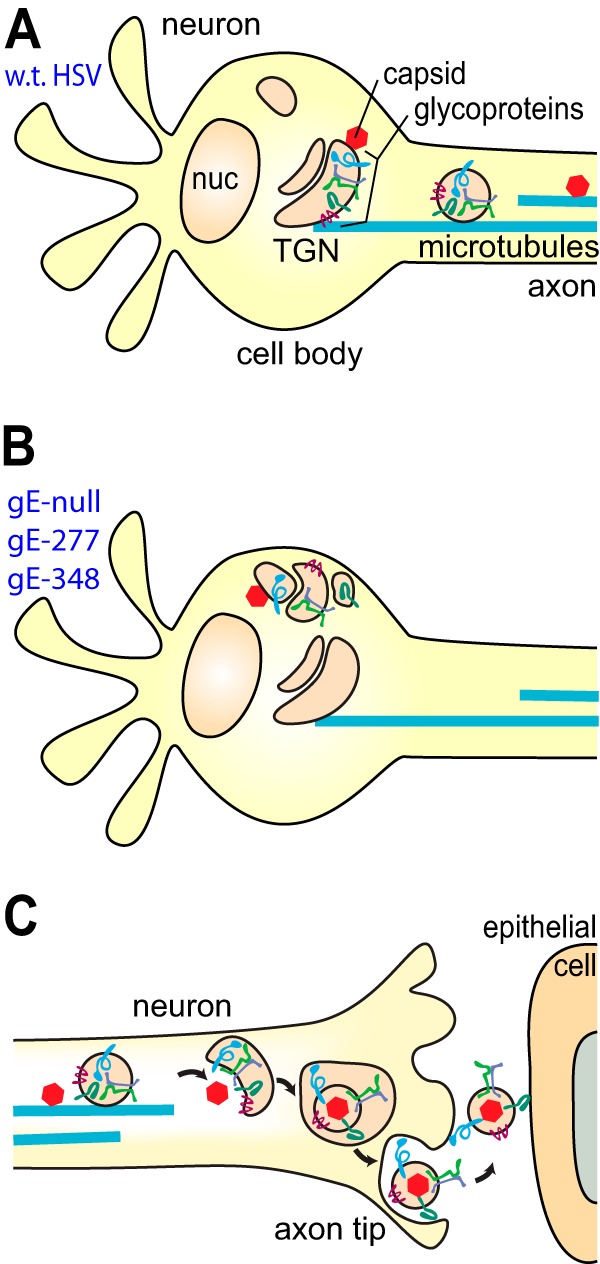
Cartoons depicting models for how gE-277 and gE-348 might fail to promote axonal transport and neuron-to-epithelial cell spread. (A) In wt HSV-infected neurons, wt HSV gE/gI ET domains promote the assembly of other glycoproteins and tegument-coated capsids into TGN-like membranes, where there is loading of viral structural proteins onto kinesin motors and microtubules. (B) In neurons infected with HSV gE-null, HSV gE-277, or HSV gE-348, viral glycoproteins and tegument-coated capsids are missorted, so assembly occurs at intracellular sites distant from where loading onto kinesins occurs. (C) Unenveloped capsids and vesicles containing glycoproteins arrive at axon tips, and secondary envelopment produces enveloped virions. Virions inside membrane vesicles must be sorted to the surfaces of axon tips, where exocytosis occurs. Extracellular virions that remain bound on axon surfaces (at axon-epithelial cell junctions) interact with epithelial cells, promoting rapid entry into epithelial cells.
