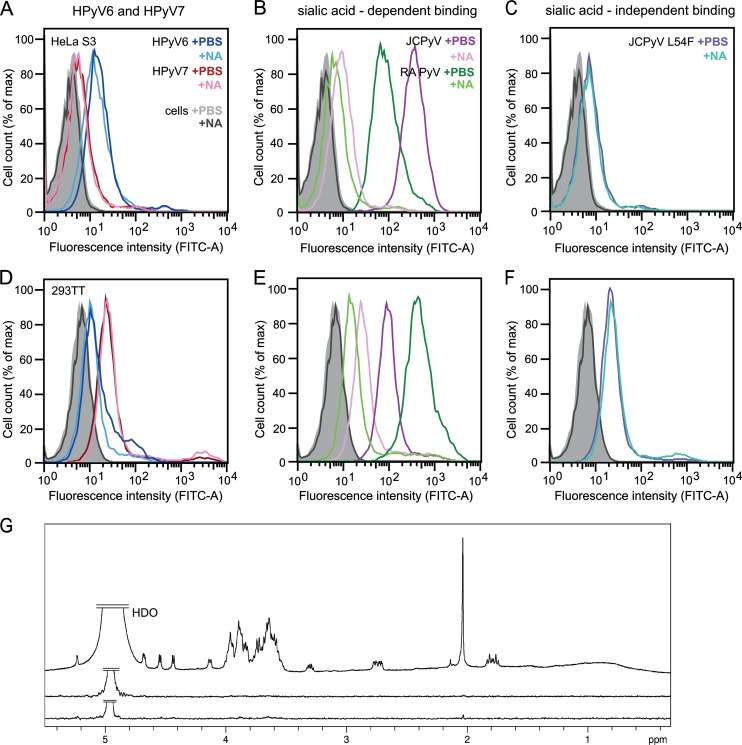
FIG 4.
HPyV6 and HPyV7 VP1 do not engage sialic acids. (A to F) Cell binding analysis. (G) Saturation transfer difference (STD) NMR spectroscopy of HPyV6 and HPyV7 VP1 pentamers with α2,3- and α2,8-sialyllactose. (A to F) HeLa S3 (A to C) and 293TT (D to F) cells were subjected to mock treatment (PBS) or were pretreated with 0.2 U/ml Clostridium perfringens neuraminidase (NA), washed, and then incubated with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated VP1 pentamers. VP1 pentamer binding was then analyzed by flow cytometry. Histograms represent the fluorescence intensity of Alexa Fluor 488 for 10,000 gated events in each case. Data for cells alone are colored gray and black for mock- and NA-treated cells, respectively. Three independent experiments were performed, and results of a typical experiment are presented. (B and E) JCPyV and murine polyomavirus (RA strain) VP1 pentamers are included as positive controls for neuraminidase-sensitive attachment (30, 51). (C and F) JCPyV L54F is a VP1 mutant with an abolished sialic acid binding site (37) and was used to test for sialic acid-independent cell binding. FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; max, maximum. (G) From top to bottom: 1H reference spectrum of 50 μM HPyV7 VP1 with 1 mM α2,3- and α2,6-sialyllactose each; STD NMR difference spectrum recorded with the same sample; STD NMR difference spectrum of 50 μM HPyV6 VP1 with 1 mM (each) α2,3- and α2,8-sialyllactose. No significant saturation transfer to either capsid protein was observed. HDO peaks were truncated for clarity.