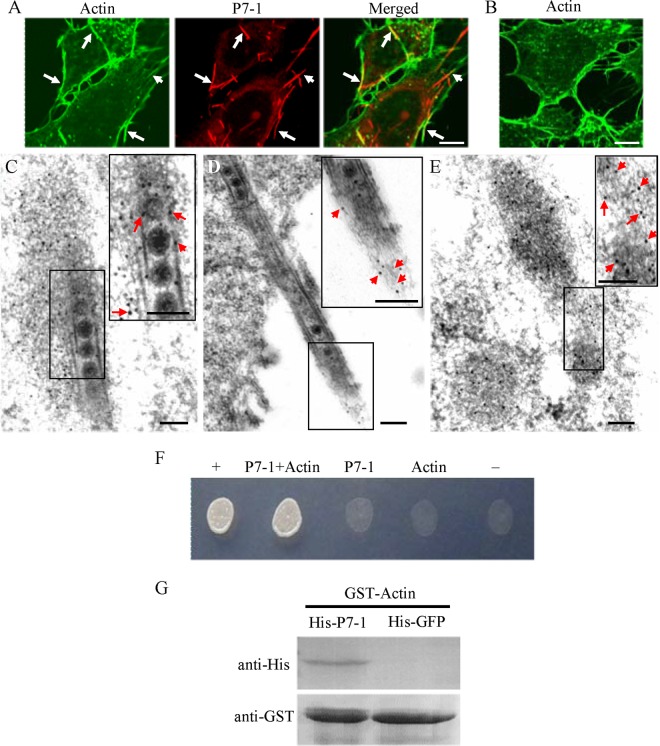
FIG 2.
Association of P7-1 tubules with actin filaments in VCMs. (A, B) Immunofluorescence micrographs of the colocalization of P7-1 tubules with actin filaments (arrows) in VCMs at 84 hpi. SRBSDV-infected (A) and mock-infected (B) VCMs were immunolabeled with the actin dye FTIC-phalloidin (green) and P7-1–rhodamine (red). Bars, 5 μm. (C to E) Immunoelectron micrographs of the association of some actin filaments with virus-containing tubules within the cytoplasm (C) or along the filopodia (D) at 84 hpi. SRBSDV-infected (C, D) and mock-infected (E) VCMs were immunolabeled with actin-specific IgG as the primary antibody, followed by treatment with 10-nm gold particle-conjugated goat antibodies against rabbit IgG as secondary antibodies. (Insets) Enlarged images of the boxed areas. Arrows, gold particles. Bars, 100 nm. (F) The interaction between P7-1 of SRBSDV and actin of the WBPH detected by yeast two-hybrid assay. Transformants on an SD-Trp-Leu-His-Ade agar plate are shown. +, positive control, i.e., pBT3-STE and pOst1-NubI; P7-1+Actin, pBT3-STE-P7-1 and pPR3-N-actin; P7-1, pBT3-STE-P7-1 and pPR3-N; Actin, pBT3-STE and pPR3-N-actin; −, negative control, i.e., pBT3-STE and pPR3-N. (G) The pulldown assay was used to detect the interaction between P7-1 of SRBSDV and actin of WBPH. P7-1 of SRBSDV was fused with His to act as a bait protein with GFP as a control. Actin of WBPH was fused with GST as a prey protein. Actin bound to His-fused P7-1 of SRBSDV, but it did not bind to His-fused GFP.