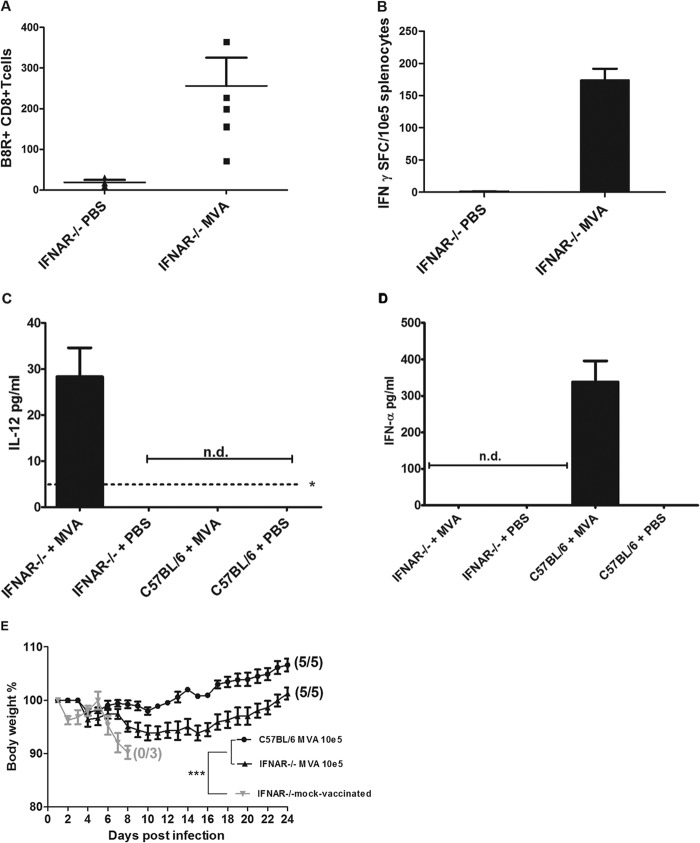
FIG 5.
MVA immunization in mice lacking the type I interferon receptor (IFNAR−/− mice). (A and B) Induction of virus-specific CD8+ T cells. IFNAR−/− mice were inoculated intramuscularly with 105 PFU MVA or PBS. (A) On day 6 after immunization, total numbers of B8R+ CD8+ T cells in blood from IFNAR−/− mice (n = 5) were determined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis. (B) At 8 days postvaccination, splenocytes were prepared, and B8R20–27-specific IFN-γ-producing CD8+ T cells were measured by ELISPOT. Data are representative of two similar experiments. (C and D) Induction of IL-12 or IFN-α in sera of MVA-vaccinated mice. (C) Serum levels of IL-12 in IFNAR−/− mice or C57BL/6 mice at 18 h postimmunization. The asterisk indicates the minimum detectable concentration of IL-12(p70) (4 pg/ml). (D) Serum levels of IFN-α in IFNAR−/− mice or C57BL/6 mice at 12 h after immunization with MVA. n.d., not detectable. (E) Protective capacity of low-dose (105 PFU) MVA vaccination in IFNAR−/− mice. Animals were infected with ECTV 2 days after vaccination with MVA or PBS (mock-vaccinated controls), and weight loss of individual mice was monitored daily (3 to 5 per group). Error bars indicate SEMs, and the numbers of surviving/total animals are given in parentheses. ***, P < 0.001.