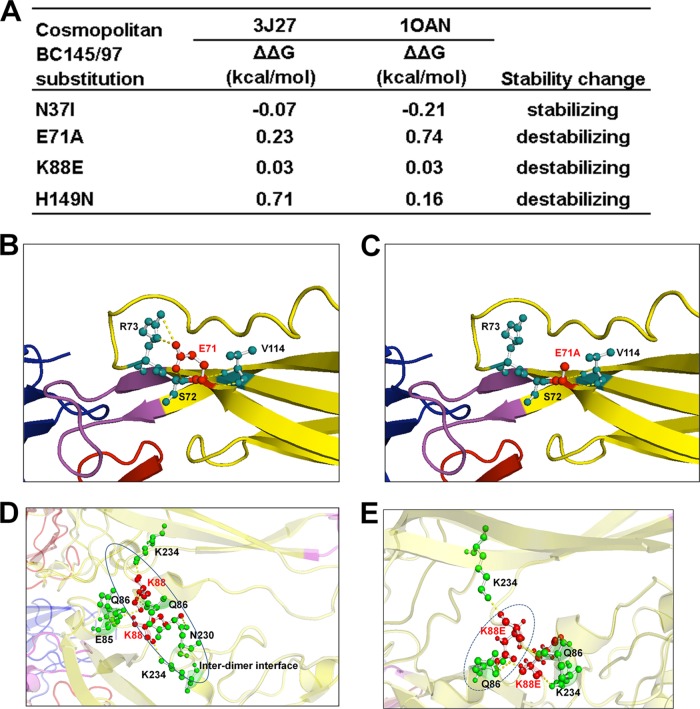
FIG 8.
Naturally occurring mutations affect the structural stability of the E protein of pVD2-Cosmopolitan VLPs. (A) Stable free energy (ΔΔG) calculations for E-protein substitutions in Cosmopolitan genotype strain BC145/97 based upon the Protein Data Bank structural coordinates for the mature dengue virus particle (PDB accession number 3J27) and soluble E protein (PDB accession number 1OAN) (25, 27). (B to E) Amino acid residues involved in E-protein intra- and interdimer polar contacts. (B) E71 (in a red ball-and-stick representation) and its intradimeric contact with amino acid residues S72, R73, and V114 (in green ball-and-stick representations), connected by yellow dashed lines. (C) The construct with the E71A substitution shows a loss of intradimeric contact with R73. (D) K88 (in a red ball-and-stick representation) and its contact with various amino acid residues (in green ball-and-stick representations), connected by yellow dashed lines. K88 of chain A of the E-protein asymmetric unit has intradimeric contacts within chain A at positions Q86 and K234 and has an interdimeric contact with E85 of chain C. K88 of chain C has intradimeric contacts within chain C at positions Q86, N230, and K234. (E) K88E of chain A shows a loss of interdimeric contact with E85 of chain C and a steric clash with Q86 of chain C. K88E of chain C shows a loss of intradimeric contact with N230 of chain C.