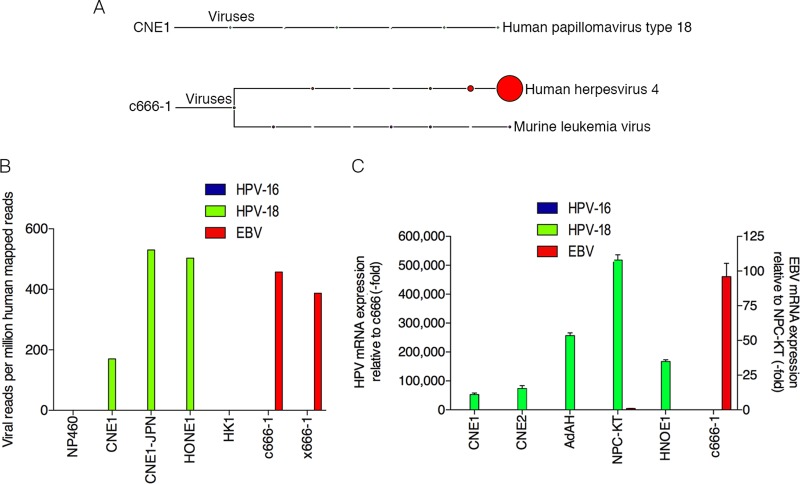
FIG 1.
Detection of human papillomavirus 18 in nasopharyngeal carcinomas. (A) RNA-seq data from each NPC sample was analyzed using RNA CoMPASS. A representative virome branch of the taxonomy tree (CNE1) for each HPV+ sample was generated using the metagenome analyzer MEGAN 4. c666-1 was positive for both EBV (human herpesvirus 4) and MuLV. (B) In-depth analysis of the virome. Raw reads from each sample were aligned to the hg19 genome with the custom human virus genome using the genome aligner STAR. Reads are displayed as viral reads per million human mapped reads. Blue, HPV-16 reads; green, HPV-18 reads; and red, EBV reads. (C) Using quantitative real-time PCR, six NPC cell lines were surveyed for the presence of HPV-16 (blue columns), HPV-18 (green columns), and EBV (red columns). Five out of the six NPC cell lines demonstrated evidence of HPV-18, but none of the NPC cell lines was infected with HPV-16. Both NPC-KT and c666-1 were positive for EBV EBER. Samples were normalized to GAPDH and compared to c666-1 for HPV-16 or -18 expression and compared to NPC-KT for EBV expression.