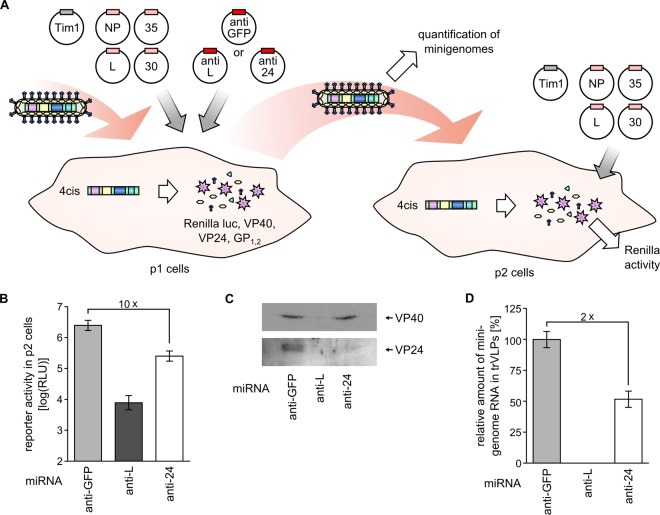
FIG 6.
Role of VP24 in RNA incorporation. (A) Experimental design. 293 cells (p1 cells) pretransfected with expression plasmids for NP, VP35, VP30, L, and Tim1 as well as miRNAs directed against L (anti-L), VP24 (anti-VP24), or an unrelated protein (anti-GFP) were infected with trVLPs containing a tetracistronic minigenome. At 72 h after infection, trVLPs produced by the p1 cells were used to infect p2 target cells that had been pretransfected with expression plasmids for NP, VP35, VP30, L, and Tim1. (B) Efficacy of miRNA knockdown. Reporter activity in p2 cells was determined 72 h after infection to confirm the efficacy of miRNA knockdown in p1 cells. The means and standard deviations from 4 independent experiments are shown. (C) Influence of VP24 on trVLP budding. trVLPs produced by p1 cells were concentrated by centrifugation through a sucrose cushion and subjected to Western blotting using antibodies against VP40 and VP24. (D) Influence of VP24 on RNA incorporation into trVLPs. Minigenome RNA in trVLPs produced by p1 cells was extracted and quantified using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. The means and standard deviations from 4 independent experiments are shown.