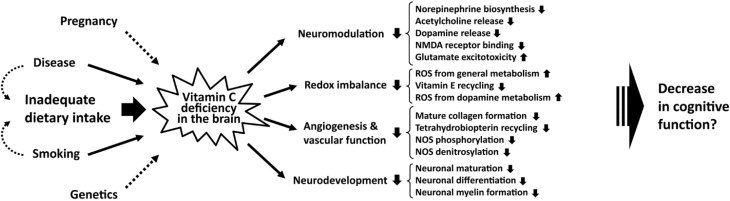
Figure 1.
Proposed causes and consequences of VitC deficiency in the brain. Several risk factors for VitC deficiency have been identified, including disease, smoking, and inadequate dietary intake, but also pregnancy and genetics have been shown to affect VitC levels. Based on VitC’s involvement in important processes in the brain, there is reason to believe that these could be adversely affected by a deficiency. The functions of VitC are both related to its antioxidant function of upholding redox balance in the brain but also other important functions. These include modulation of the cholinergic, catecholinergic, and glutamergic systems of the brain, as well as the general development of neurons through maturation, differentiation and myelin formation. VitC is involved in several processes in the vascular system and hereby help maintain integrity and function of, e.g., nitric oxide synthase, which regulates vessel relaxation through production of nitric oxide. Abbreviations: NOS, nitric oxide synthase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NMDA, N-methyl-d-aspartate.