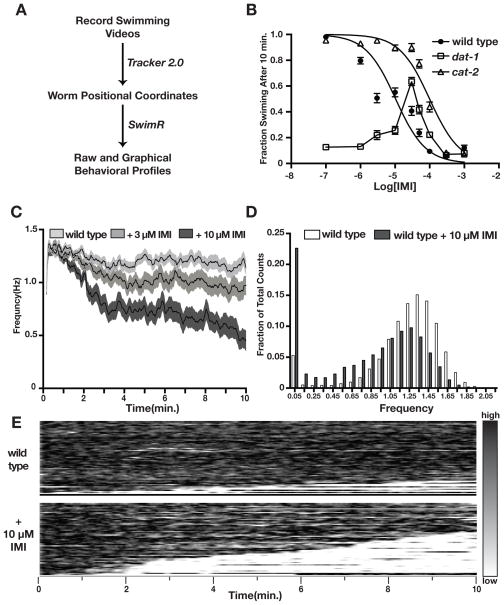
Figure 1.
Paralytic effects of IMI on C. elegans wild type (N2) animals as determined by manual and automated assays. A) Diagram of the workflow for C. elegans swimming analysis. B) Response of wild type (filled circles), cat-2 (open triangles), and dat-1 (open squares) to increasing concentrations of IMI. Dose-response data points for dat-1 were connected with a line between data points. C) Effect of IMI on swimming frequency of wild type animals. Shaded areas represent SEM. 3 μM IMI triggered a significant (P<.05) decrease in the average frequency beginning at the 4th minute (P<.05). 10 μM IMI induced a significant decrease in average frequency (P<.05) with individual time points reaching significance in the 2nd minute. D) Distribution of wild type swimming frequency values in the presence or absence of IMI (10 μM). IMI treatment induces a shift to lower frequency values. E) Heat map representations of wild type swimming frequency wjth or without 10 μM IMI.