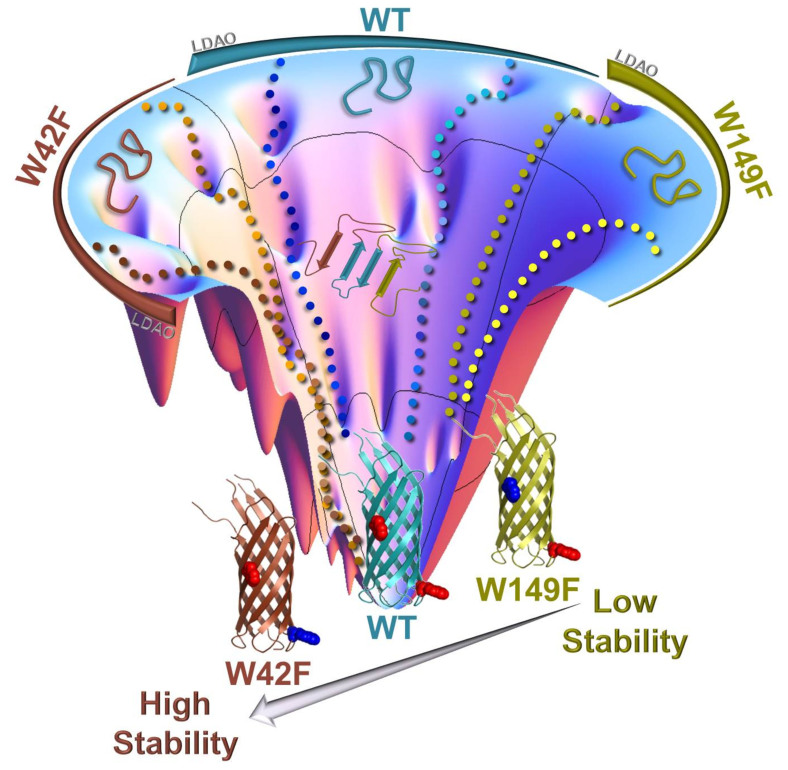
Figure 6. Schematic highlighting the contribution of W42 and W149 in the folding and stability of Ail in LDAO micelles.
WT Ail (blue/cyan) is shown in the center, W42F (brown) is shown to the left and W149F (green/yellow) to the right of the folding funnel. Dotted lines depict possible folding pathways on the folding funnel (generated using a Mathematica® notebook available at www.oaslab.com). W42 of Ail plays a key role in driving barrel refolding and therefore mutation of this residue populates refolding intermediates during barrel formation, as depicted here for the W42F mutant (brown). Furthermore, presence of only W42 (in the W149F mutant) lowers the incidence of stable intermediates in the refolding pathway. In all three proteins, increasing the LDAO concentration affects the folding efficiency by stabilizing the on-pathway intermediates. Once folded, barrel stability is determined by W149, and the three proteins now follow the order W42F > WT > W149F. The most favorable free energy minimum in LDAO micelles is achieved in the Ail barrel possessing a single W149 in the transmembrane region.